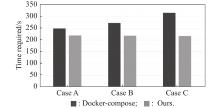
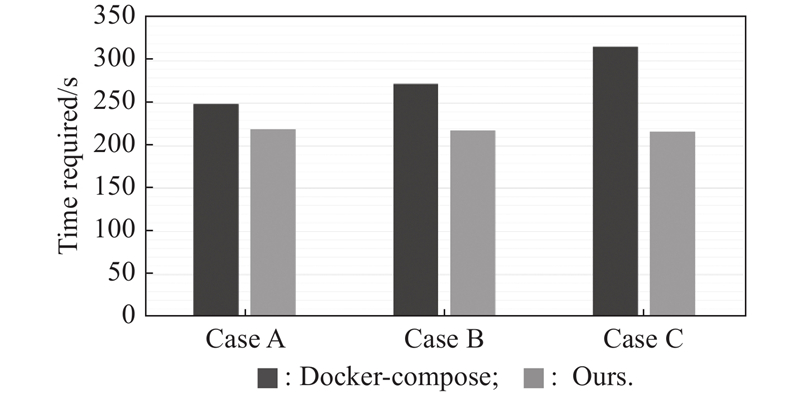
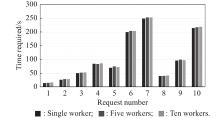
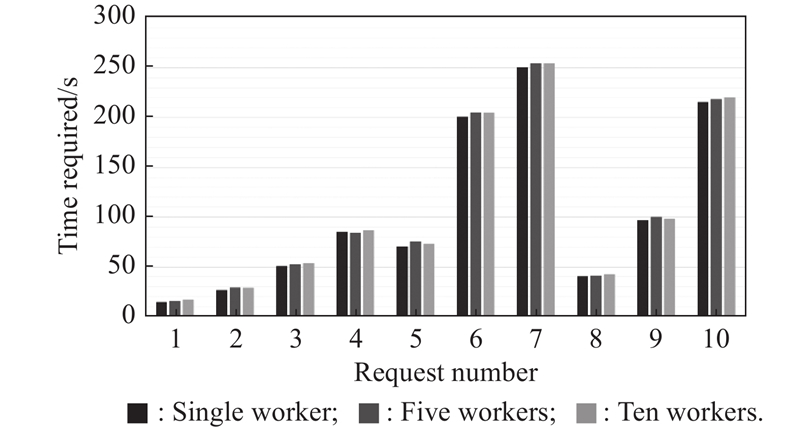
| 1 |
MERKEL D. Docker: lightweight linux containers for consistent development and deployment. Linux Journal, 2014. https://www.linuxjournal.com/content/docker-lightweight-linux-containers-consistent-development-and-deployment.
|
| 2 |
SMET P, DHOEDT B, SIMOENS P Docker layer placement for on-demand provisioning of services on edge clouds. IEEE Trans. on Network and Service Management, 2018, 15 (3): 1161- 1174.
doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2018.2844187
|
| 3 |
SINGH S, SINGH N. Containers & Docker: emerging roles & future of Cloud technology. Proc. of the 2nd International Conference on Applied and Theoretical Computing and Communication Technology, 2016: 804−807.
|
| 4 |
MERELLI I, FORNARI F, TORDINI F, et al Exploiting Docker containers over Grid computing for a comprehensive study of chromatin conformation in different cell types. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2019, 134, 116- 127.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2019.08.002
|
| 5 |
PAHL C Containerization and the paas cloud. IEEE Cloud Computing, 2015, 2 (3): 24- 31.
doi: 10.1109/MCC.2015.51
|
| 6 |
THALHEIM J, BHATOTIA P, FONSECA P, et al. CNTR: lightweight {OS} containers. Proc. of the {USENIX} Annual Technical Conference ({USENIX}{ATC} 18), 2018: 199−212.
|
| 7 |
PENG Y H, BAO Y X, CHEN Y R, et al Dl2: a deep learning-driven scheduler for deep learning clusters. IEEE Trans. on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2021, 32 (8): 1947- 1960.
doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2021.3052895
|
| 8 |
WU Y D, MA K H, YAN X, et al Elastic deep learning in multi-tenant GPU clusters. IEEE Trans. on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2021, 33 (1): 144- 158.
|
| 9 |
ZHOU Q H, GUO S, QU Z H, et al Petrel: heterogeneity-aware distributed deep learning via hybrid synchronization. IEEE Trans. on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2020, 32 (5): 1030- 1043.
|
| 10 |
ZHAO N N, TARASOV V, ALBAHAR H, et al Large-scale analysis of docker images and performance implications for container storage systems. IEEE Trans. on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2020, 32 (4): 918- 930.
|
| 11 |
LEE C, KIM S, KIM E A deduplication-enabled P2P protocol for VM image distribution. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, 2015, 98 (5): 1108- 1111.
|
| 12 |
DU L, WO T Y, YANG R Y, et al. Cider: a rapid docker container deployment system through sharing network storage. Proc. of the IEEE 19th International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications, IEEE 15th International Conference on Smart City, IEEE 3rd International Conference on Data Science and Systems, 2017: 332−339.
|
| 13 |
ZHANG S Q, WU S, FAN H, et al. BED: a block-level deduplication-based container deployment framework. Proc. of the International Conference on Green, Pervasive, and Cloud Computing, 2020: 504−518.
|
| 14 |
ZHAO X, ZHANG Y, WU Y W, et al Liquid: a scalable deduplication file system for virtual machine images. IEEE Trans. on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2013, 25 (5): 1257- 1266.
|
| 15 |
SAHARAN S, SOMANI G, GUPTA G, et al QuickDedup: efficient VM deduplication in cloud computing environments. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2020, 139, 18- 31.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2020.01.002
|
| 16 |
HARTER T, SALMON B, LIU R, et al. Slacker: fast distribution with lazy docker containers. Proc. of the 14th {USENIX} Conference on File and Storage Technologies, 2016: 181−195.
|
| 17 |
CIVOLANI L, PIERRE G, BELLAVISTA P. FogDocker: start container now, fetch image later. Proc. of the 12th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing, 2019: 51−59.
|
| 18 |
ZHENG C, RUPPRECHT L, TARASOV V, et al. Wharf: sharing docker images in a distributed file system. Proc. of the ACM Symposium on Cloud Computing, 2018: 174−185.
|
| 19 |
CHEN J L, LIAQAT D, GABEL M, et al. Poster: an accelerator for fast container-based applications deployment on the edge. Proc. of the IEEE/ACM Symposium on Edge Computing, 2020: 175−177.
|
| 20 |
AHMED A, PIERRE G. Docker container deployment in fog computing infrastructures. Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Edge Computing, 2018: 1−8.
|
| 21 |
PENG C Y, KIM M, ZHANG Z, et al. VDN: virtual machine image distribution network for cloud data centers. 2012 Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM, 2012: 181−189.
|
| 22 |
ZHANG Z N, LI Z Y, WU K, et al VMThunder: fast provisioning of large-scale virtual machine clusters. IEEE Trans. on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2014, 25 (12): 3328- 3338.
doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2014.7
|
| 23 |
LIANG M Y, SHEN S Q, LI D S, et al. HDID: an efficient hybrid docker image distribution system for datacenters. Proc. of the National Software Application Conference, 2016: 179−194.
|
| 24 |
WANG K J, YANG Y, LI Y, et al. Fid: a faster image distribution system for docker platform. Proc. of the IEEE 2nd International Workshops on Foundations and Applications of Self* Systems, 2017: 191−198.
|
| 25 |
NATHAN S, GHOSH R, MUKHERJEE T, et al. Comicon: a co-operative management system for docker container images. Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Cloud Engineering, 2017: 116−126.
|
 ), Junjiang LI1,2(
), Junjiang LI1,2( ), Can CHEN2,3(
), Can CHEN2,3( ), Dengyin ZHANG1,2,*(
), Dengyin ZHANG1,2,*( )
)