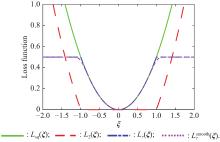
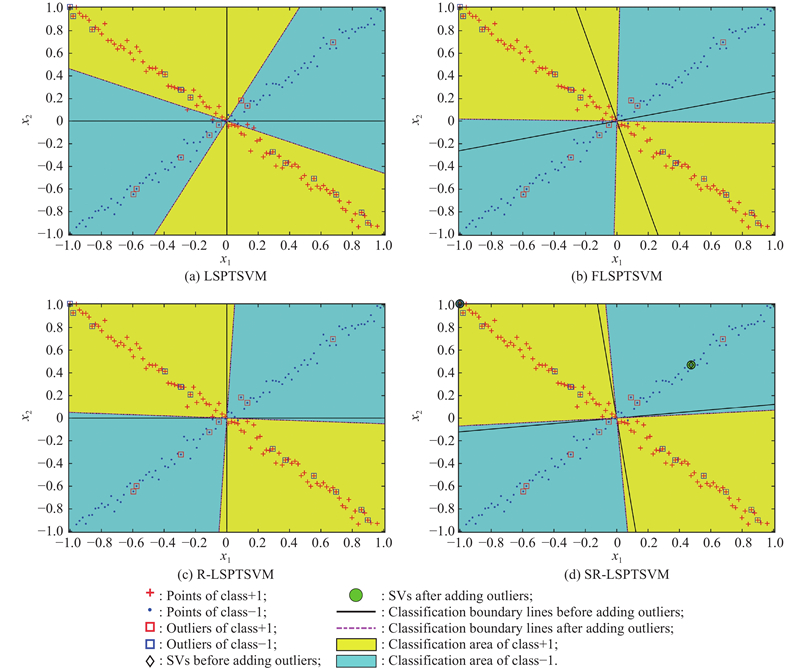
Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2023, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (4): 827-838.doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2023.000103
• • 上一篇
-
收稿日期:2022-04-13接受日期:2023-06-15出版日期:2023-08-18发布日期:2023-08-28
Robust least squares projection twin SVM and its sparse solution
Shuisheng ZHOU1( ), Wenmeng ZHANG1(
), Wenmeng ZHANG1( ), Li CHEN2,3,*(
), Li CHEN2,3,*( ), Mingliang XU3(
), Mingliang XU3( )
)
- 1 School of Mathematics and Statistics, Xidian University, Xi’an 710126, China
2 School of Physical Education, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, China
3 School of Computer and Artificial Intelligence, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, China
-
Received:2022-04-13Accepted:2023-06-15Online:2023-08-18Published:2023-08-28 -
Contact:Li CHEN E-mail:sszhou@mail.xidian.edu.cn;3137710140@qq.com;cli@zzu.edu.cn;iexumingliang@zzu.edu.cn -
About author:
ZHOU Shuisheng was born in 1972. He received his M.S. degree in applied mathematics and Ph.D. degree in computer science from Xidian University, Xi ’an, China, in 1998 and 2005, respectively. He is currently a professor in the School of Mathematics and Statistics, Xidian University. His current research interests include optimization algorithm and its application, machine learning, pattern recognition, kernel-based learning, and support vector machines. E-mail: sszhou@mail.xidian.edu.cn
ZHANG Wenmeng was born in 1996. She received her degree in the School of Mathematics and Statistics, Xidian University. Her current research interests include optimization algorithm and its application, machine learning, pattern recognition, kernel-based learning, and support vector machines. E-mail: 3137710140@qq.com
CHEN Li was born in 1982. She received her Ph.D. degree in School of Mathematics and Statistics, Xidian University, Xi ’an, China and M.S. degree in mathematics from China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, in 2019 and 2009, respectively. She is currently an associate professor in Zhengzhou University. Her current research interests include optimization algorithm and its application, machine learning, pattern recognition, and support vector machines. E-mail: cli@zzu.edu.cn
XU Mingliang was born in 1981. He received his Ph.D. degree from the State Key Lab of Computer Aided Design and Computer Graphics, Zhejiang University, China. He is a professor in the School of Computer and Artificial Intelligence, Zhengzhou University, China. His current research interests include computer graphics, multimedia and artificial intelligence. E-mail: iexumingliang@zzu.edu.cn -
Supported by:This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61772020;62202433;62172371;62272422;62036010), the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (22100002), and the Postdoctoral Research Grant in Henan Province (202103111)
引用本文
. [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 34(4): 827-838.
Shuisheng ZHOU, Wenmeng ZHANG, Li CHEN, Mingliang XU. Robust least squares projection twin SVM and its sparse solution[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 34(4): 827-838.
"
| Data | Algorithm | 0% outliers | 10% outliers | |||||
| nSVs | Time/s | Accuracy/% | nSVs | Time/s | Accuracy/% | |||
| Hepatitis m = 124 l = 31 n = 19 | RPTSVM LSPTSVM FLSPTSVM SR-LSSVM R-LSPTSVM SR-LSPTSVM | 95(0) 124(0) 22.6(19.9) 2.4(2.6) 62(56.8) 4.8(2.7) | 0.02(0.01) 0.02(0.01) 0.07(0.01) 0.00(0.00) 0.03(0.01) 0.00(0.00) | 90.32(0) 89.25(0.03) 86.45(0.04) 90.32(0) 90.32(0) 90.32(0) | 69.7(14.5) 124(0) 26.7(42.7) 4.8(2.7) 82(32.1) 1.3(1.8) | 0.03(0.01) 0.01(0.01) 0.07(0.01) 0.00(0.00) 0.03(0.03) 0.01(0.02) | 85.81(0.04) 89.03(0.03) 80.64(0.09) 89.03(0.02) 90.32(0.04) 90.97(0.01) | |
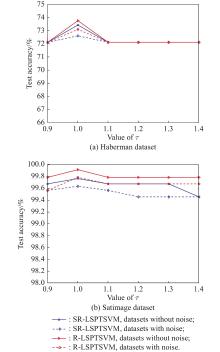
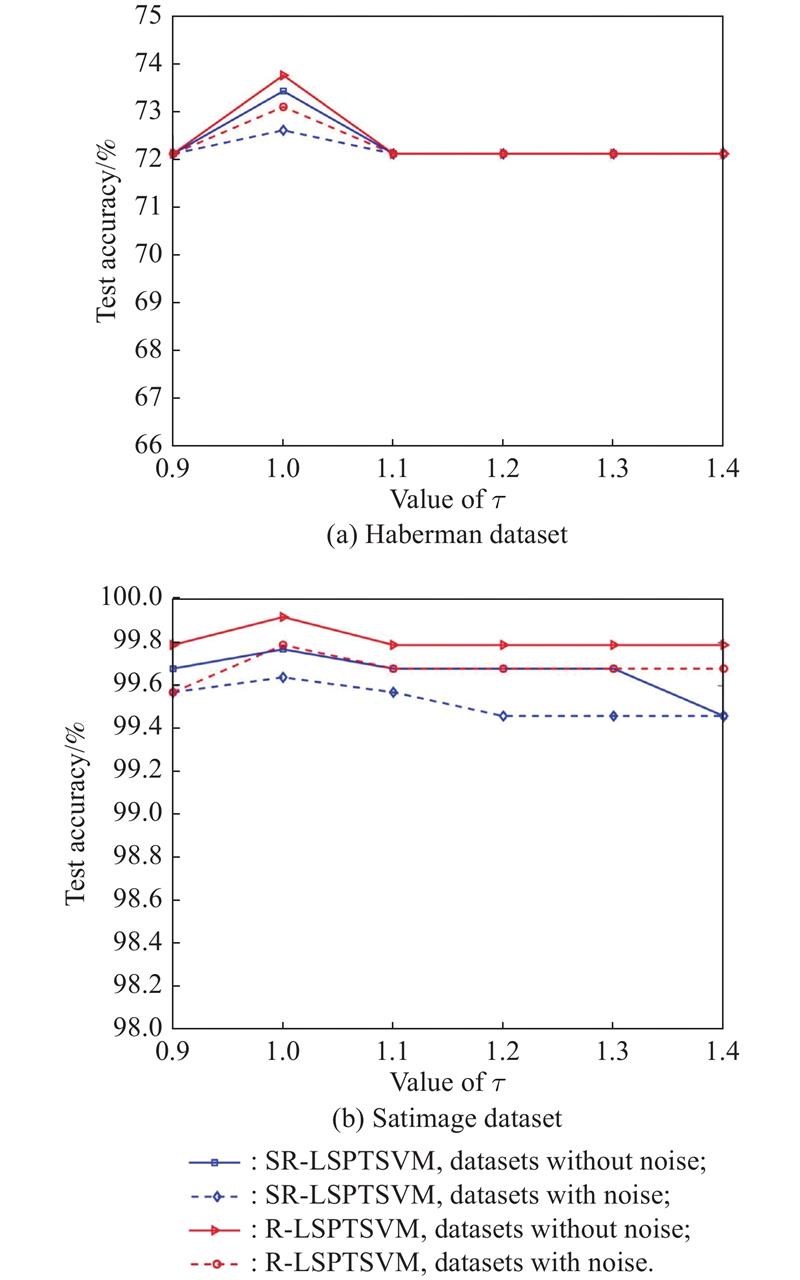
| Haberman m = 245 l = 61 n = 3 | RPTSVM LSPTSVM FLSPTSVM SR-LSSVM R-LSPTSVM SR-LSPTSVM | 173.2(11.6) 245(0) 35(5.5) 7.2(6.6) 166.6(28.6) 10(0) | 0.05(0.02) 0.02(0.01) 0.18(0.08) 0.01(0.00) 0.11(0.01) 0.01(0.00) | 70.82(0.02) 71.80(0.02) 70.82(0.03) 72.13(0) 73.77(0) 73.44(0.01) | 162.5(8.4) 245(0) 72.6(21.0) 8.6(5.0) 89.1(79.0) 4.3(3.1) | 0.04(0.02) 0.02(0.01) 0.17(0.07) 0.00(0.00) 0.03(0.03) 0.01(0.00) | 70.00(0.02) 71.47(0.04) 70.00(0.02) 72.13(0) 73.11(0.02) 72.62(0.01) | |
| Breast m = 547 l = 136 n = 10 | RPTSVM LSPTSVM FLSPTSVM SR-LSSVM R-LSPTSVM SR-LSPTSVM | 123.2(86.4) 547(0) 62(0) 27(0) 197(0) 8(0) | 0.10(0.01) 0.22(0.00) 0.64(0.05) 0.01(0.00) 0.07(0.00) 0.01(0.00) | 97.06(0.01) 97.79(0.01) 98.53(0) 98.53(0) 98.53(0) 97.79(0) | 269.7(67.4) 547(0) 3.6(4.8) 27(0) 226.5(129.0) 21.7(8.6) | 0.10(0.01) 0.23(0.10) 0.64(0.56) 0.00(0.00) 0.16(0.09) 0.01(0.02) | 94.19(0.01) 97.50(0.01) 97.94(0.01) 97.20(0.01) 98.53(0.01) 97.72(0.00) | |
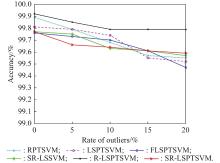
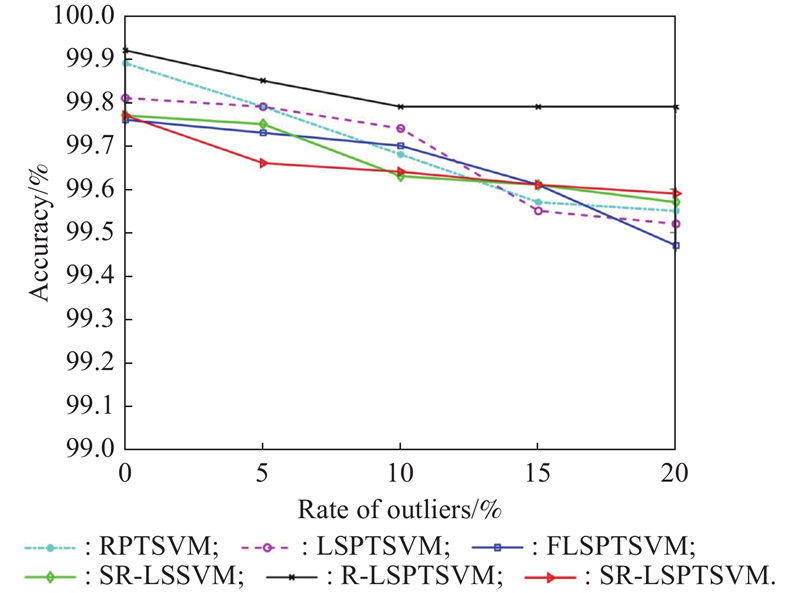
| Satimage m = 2110 l = 931 n = 36 | RPTSVM LSPTSVM FLSPTSVM SR-LSSVM R-LSPTSVM SR-LSPTSVM | 47.4(5.0) 2110(0) 59.4(54.3) 105(0) 1073.4(54.3) 105(0) | 3.60(0.11) 0.98 (0.06) 20.43(1.75) 0.06(0.01) 1.23(0.05) 0.07(0.00) | 99.89(0) 99.81(0.00) 99.76(0.00) 99.77(0.00) 99.92(0.00) 99.77(0.00) | 1053.8(164.0) 2110(0) 115.4(201.1) 105(0) 1887.6(664.6) 111(11.3) | 3.03(1.30) 1.10(0.18) 21.37(1.84) 0.14(0.08) 1.67(0.20) 0.08(0.03) | 99.68(0.00) 99.74(0.00) 99.70(0.00) 99.63(0.00) 99.79(0.00) 99.64(0.00) | |
| USPS m = 2199 l = 623 n = 256 | RPTSVM LSPTSVM FLSPTSVM SR-LSSVM R-LSPTSVM SR-LSPTSVM | 14(0) 2199(0) 59.5(16.3) 109(0) 1044(0) 109(0) | 4.06(0.84) 3.17(0.60) 26.79(0.05) 1.01(0.03) 11.47(0.22) 0.84(0.10) | 99.36(0) 99.52(0) 99.44(0.00) 99.52(0) 99.36(0) 99.20(0) | 681.9(208.6) 2199(0) 34.4(51.4) 109(0) 907.7(1130.2) 65.2(35.8) | 4.25(0.89) 3.52(0.75) 20.43(0.40) 0.48(0.06) 2.08(1.64) 0.33(0.03) | 98.65(0.01) 98.74(0.01) 98.62(0.01) 99.12(0.00) 98.65(0.00) 99.15(0.01) | |
| Shuttle m = 9206 l = 2964 n = 9 | RPTSVM LSPTSVM FLSPTSVM SR-LSSVM R-LSPTSVM SR-LSPTSVM | 1219(1707.0) 9206(0) 152.4(65.2) 50.2(5.0) 4596(0) 138.2(34.1) | 88.65(0.35) 39.25(0.35) 1796.35(0.57) 0.04(0.00) 48.25(1.17) 0.32(0.09) | 100(0) 100(0) 99.95(0.00) 99.97(0) 99.93(0) 100(0) | 3157.0(2788.0) 9206(0) 182.3(70.4) 126.8(84.3) 4002.3(687.5) 88.2(12.0) | 114.67(23.44) 39.39 (0.50) 1821.20(40.05) 0.33 (0.31) 36.42(0.24) 0.09 (0.02) | 99.88(0.00) 99.87(0.00) 99.87(0.01) 99.89(0.00) 99.91(0.00) 99.93(0) | |
| Ijcnn1 m = 35000 l = 91701 n = 22 | RPTSVM LSPTSVM FLSPTSVM SR-LSSVM R-LSPTSVM SR-LSPTSVM | — — — 1750(0) — 1750(0) | — — — 28.28(1.10) — 26.78(3.33) | — — — 90.50(0) — 90.50(0) | — — — 1750(0) — 1750(0) | — — — 28.68(1.67) — 26.39(0.23) | — — — 90.50(0) — 90.50(0) | |
| Skin- nonskin m = 61265 l = 183792 n = 3 | RPTSVM LSPTSVM FLSPTSVM SR-LSSVM R-LSPTSVM SR-LSPTSVM | — — — 3061(2.31) — 2532.2(21.4) | — — — 128.39(0.86) — 115.23(4.84) | — — — 97.67(0.01) — 98.02(0.00) | — — — 3063(0) — 2661(9.4) | — — — 115.25(0.26) — 114.28(0.60) | — — — 94.49(0.01) — 95.17(0) | |
"
| Data | Algorithm | nSVs | Time/s | Accuracy/% |
| Iris m = 120 l = 30 n = 4 k = 3 | RPTSVM LSPTSVM FLSPTSVM R-LSPTSVM SR-LSPTSVM | 74.1(4.4) 120(0) 8.8(1.7) 79.1(3.7) 6(0) | 0.02(0.00) 0.01(0.00) 0.04(0.00) 0.01(0.01) 0.00(0.00) | 93.33(0) 96.33(0.03) 92.33(0.02) 96.34(0.02) 96.33(0.02) |
| Wine m = 143 l = 35 n = 13 k = 3 | RPTSVM LSPTSVM FLSPTSVM R-LSPTSVM SR-LSPTSVM | 117.9(3.8) 143(3.0) 33.0(3.5) 119.1(2.8) 18.3(3.1) | 0.04(0.00) 0.02(0.00) 0.08(0.00) 0.01(0.00) 0.00(0.00) | 100(0) 100(0) 98.86(0.01) 100(0) 100(0) |
| Vehicle m = 677 l = 169 n = 18 k = 4 | RPTSVM LSPTSVM FLSPTSVM R-LSPTSVM SR-LSPTSVM | 290.4(10.7) 677(0) 49.8(3.7) 579.5(12.3) 33(0) | 0.54(0.06) 0.38(0.01) 1.13(0.04) 0.05(0.00) 0.01(0.01) | 82.72(0.02) 77.04(0.02) 70.60(0.02) 83.14(0.01) 73.96(0.00) |
| Segment m = 1848 l = 462 n = 19 k = 7 | RPTSVM LSPTSVM FLSPTSVM R-LSPTSVM SR-LSPTSVM | 453.6(9.2) 1848(0) 137.4(3.5) 1828.7(18.0) 91.9(0.3) | 2.98(0.05) 10.8(0.16) 3.72(0.08) 0.29(0.01) 0.09(0.00) | 94.67(0.01) 95.61(0.00) 95.26(0.00) 96.23(0.01) 93.77(0.00) |
| Pendigits m = 7494 l = 3498 n = 16 k = 10 | RPTSVM LSPTSVM FLSPTSVM R-LSPTSVM SR-LSPTSVM | 846.6(24.2) 7494(0) 500.4(2.0) 7342.1(21.2) 374(0) | 5.54(0.24) 18.59(5.55) 137.34(4.80) 2.95(0.06) 1.11(0.01) | 98.03(0.00) 97.45(0.00) 86.99(0.04) 98.08(0.00) 98.05(0.00) |
| 1 | CORTES C, VAPNIK V Support-vector networks. Machine Learning, 1995, 20 (3): 273- 297. |
| 2 | BURGES C A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 1998, 2 (6): 121- 167. |
| 3 | OSUNA E, FREUND R, GIROSI F. Training support vector machines: an application to face detection. Proc. of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, 2000: 130–136. |
| 4 | TRAFALIS T B, INCE H. Support vector machine for regression and applications to financial forecasting. Proc. of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2000: 348–353. |
| 5 |
CALISIR D, DOGANTEKIN E A new intelligent hepatitis diagnosis system: PCA-LSSVM. Expert Systems with Applications, 2011, 38 (8): 10705- 10708.
doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2011.01.014 |
| 6 | ZHANG S J, YANG R, LIU S Y, et al Coupled compressed sensing inspired sparse spatial-spectral LSSVM for hyperspectral image classification. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2015, 79 (5): 80- 89. |
| 7 |
KHEMCHANDANI R, CHANDRA S Twin support vector machines for pattern classification. IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29 (5): 905- 910.
doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1068 |
| 8 |
KUMAR M A, GOPAL M Application of smoothing technique on twin support vector machines. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2008, 29 (13): 1842- 1848.
doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2008.05.016 |
| 9 |
CHEN X B, YANG J, YE Q L, et al Recursive projection twin support vector machine via within-class variance minimization. Pattern Recognition, 2011, 44 (10/11): 2643- 2655.
doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2011.03.001 |
| 10 |
SHAO Y H, DENG N Y, YANG Z M Least squares recursive projection twin support vector machine for classification. Pattern Recognition, 2012, 45 (6): 2299- 2307.
doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2011.11.028 |
| 11 | DING S F, HUA X P Recursive least squares projection twin support vector machines for nonlinear classification. Neurocomputing, 2014, 130 (4): 3- 9. |
| 12 | SUYKENS J, LUKAS L, VANDEWALLE J. Sparse approximation using least squares support vector machines. Proc. of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2002: 757–760. |
| 13 |
JIAO L C, BO L F, WANG L Fast sparse approximation for least squares support vector machine. IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks, 2007, 18 (3): 685- 697.
doi: 10.1109/TNN.2006.889500 |
| 14 | ZHOU S S Sparse LSSVM in primal using cholesky factorization for large-scale problems. IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks & Learning Systems, 2016, 27 (4): 783- 795. |
| 15 | ZHOU S S, LIU M. A new sparse LSSVM method based the revised LARS. Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Machine Vision & Information Technology, 2017: 46–51. |
| 16 |
CHENG R J, SONG Y D, CHEN D W, et al Intelligent localization of a high-speed train using LSSVM and the online sparse optimization approach. IEEE Trans. on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18 (8): 2071- 2084.
doi: 10.1109/TITS.2016.2633344 |
| 17 |
SUN B B, NG W W Y, YEUNG D S Improved sparse LSSVMS based on the localized generalization error model. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2017, 8 (6): 1853- 1861.
doi: 10.1007/s13042-016-0563-6 |
| 18 |
MA Y F, LIANG X, SHENG G, et al Noniterative sparse LS-SVM based on globally representative point selection. IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32 (2): 788- 798.
doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2979466 |
| 19 | SUYKENS J A K, BRABANTER J D, LUKAS L, et al Weighted least squares support vector machines: robustness and sparse approximation. Neurocomputing, 2002, 48 (1): 85- 105. |
| 20 | WEI L W, CHEN Z Y, LI J P, et al. Sparse and robust least squares support vector machine: a linear programming formulation. Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Grey Systems and Intelligent Services, 2007: 1134–1138. |
| 21 |
WEN W, HAO Z F, YANG X W, et al Robust least squares support vector machine based on recursive outlier elimination. Soft Computing, 2010, 14 (11): 1241- 1251.
doi: 10.1007/s00500-009-0535-9 |
| 22 | YANG X W, TAN L J, HE L F A robust least squares support vector machine for regression and classification with noise. Neurocomputing, 2014, 140 (22): 41- 52. |
| 23 | CHEN L, ZHOU S S Sparse algorithm for robust LSSVM in primal space. Neurocomputing, 2018, 275 (1): 2880- 2891. |
| 24 | YE Y F, SHAO Y H, DENG N Y, et al Robust Lp-norm least squares support vector regression with feature selection . Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2017, 305 (6): 32- 52. |
| 25 | LU X J, LIU W B, ZHOU C, et al Robust least-squares support vector machine with minimization of mean and variance of modeling error. IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks & Learning Systems, 2018, 29 (7): 2909- 2920. |
| 26 | ZHOU S S, ZHOU W D Unified SVM algorithm based on LS-DC loss. Machine Learning, 2021, 31 (4): 1- 28. |
| 27 | SCHLKOPF B, HERBRICH R, SMOLA A J A generalized representer theorem. Berlin: Springer, 2001. |
| 28 | SHALEV-SHWARTZ S, BEN-DAVID S. Understanding machine learning: from theory to algorithms. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2014. |
| 29 |
YUILLE A L, RANGARAJAN A The concave convex procedure. Neural Computation, 2003, 15 (4): 915- 936.
doi: 10.1162/08997660360581958 |
| 30 | TAO P D, LE T Convex analysis approach to d.c. programming: theory, algorithm and applications. Acta Mathematica Vietnamica, 1997, 22 (1): 289- 355. |
| 31 | WANG K N, ZHONG P Robust non-convex least squares loss function for regression with outliers. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2014, 71 (1): 290- 302. |
| 32 | ZHOU S S, CUI J T, YE F, et al New smoothing SVM algorithm with tight error bound and efficient reduced techniques. Computational Optimization & Applications, 2013, 56 (3): 599- 617. |
| 33 |
HE B S, YUAN X M On the O(1/n) convergence rate of the Douglas-Rachford alternating direction method . SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 2012, 50 (2): 700- 709.
doi: 10.1137/110836936 |
| 34 | SHAO Y H, WANG Z, CHEN W J, et al A regularization for the projection twin support vector machine. Knowledge- Based Systems, 2013, 37 (2): 203- 210. |
| 35 | GUO J H, YI P, WANG R L, et al Feature selection for least squares projection twin support vector machine. Neurocomputing, 2014, 144 (11): 174- 183. |
| 36 |
SHAO Y H, ZHANG C H, WANG X B, et al Improvements on twin support vector machines. IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks, 2011, 22 (6): 962- 968.
doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2130540 |
| 37 | CHANG C C, LIN C J. LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||