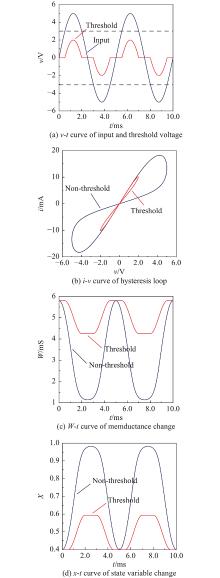
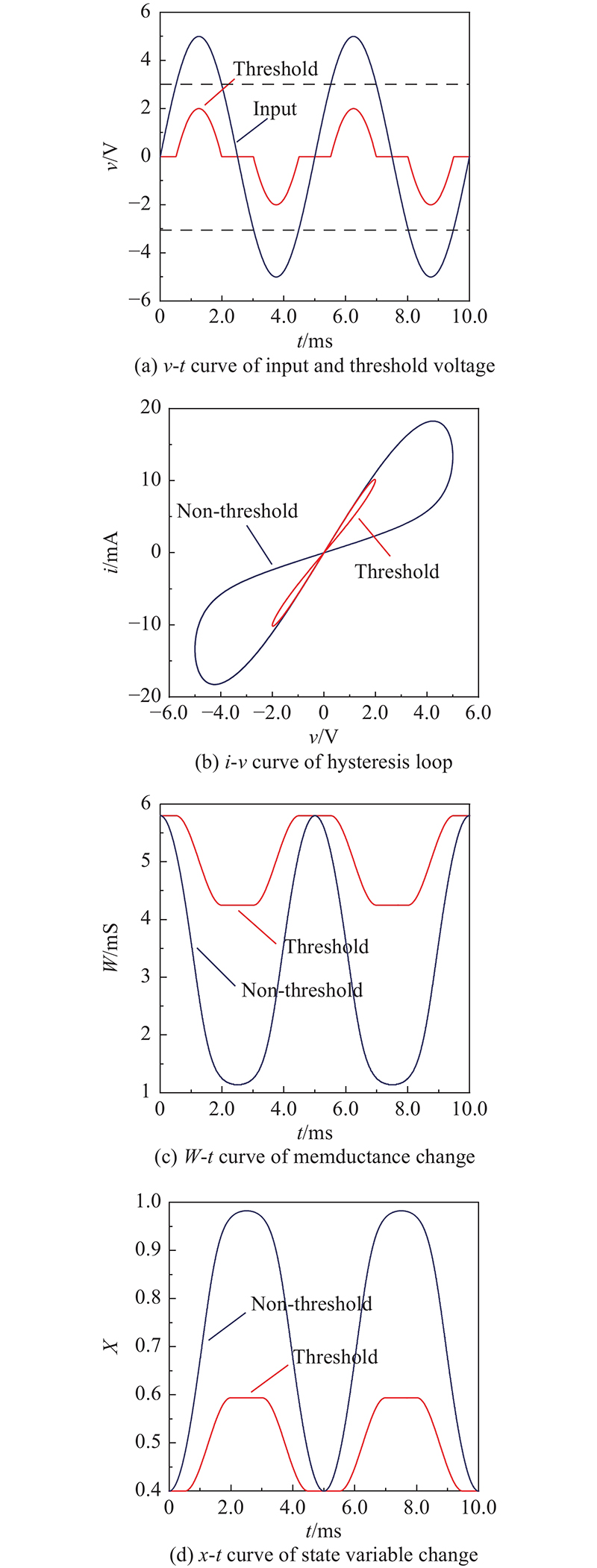
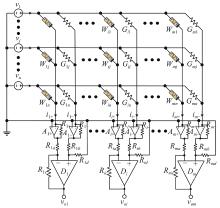
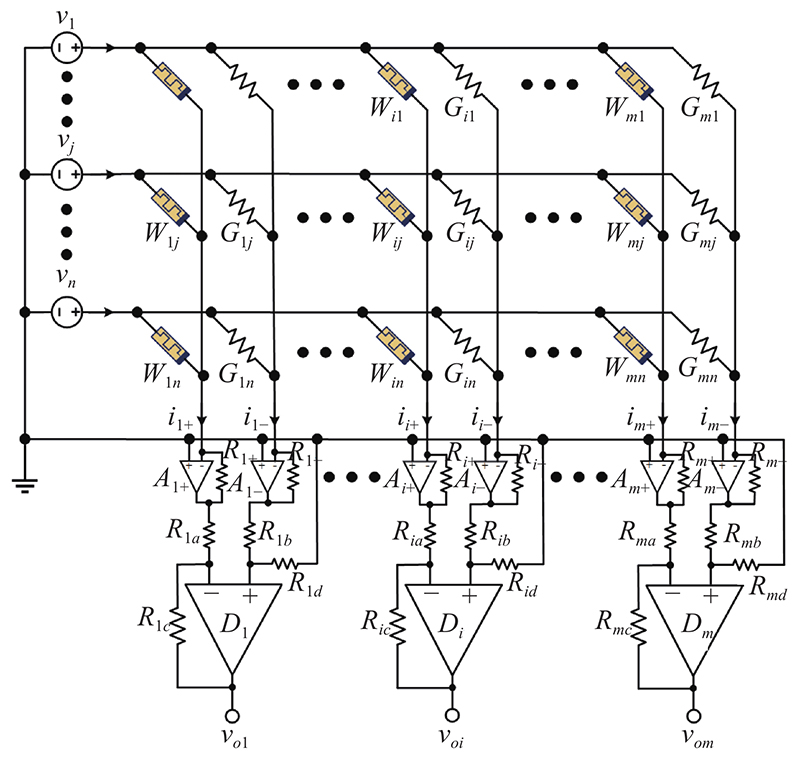
Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2023, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 324-334.doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2023.000018
• • 上一篇
-
收稿日期:2021-09-27出版日期:2023-04-18发布日期:2023-04-18
Threshold-type memristor-based crossbar array design and its application in handwritten digit recognition
Qingjian LI, Yan LIANG( ), Zhenzhou LU(
), Zhenzhou LU( ), Guangyi WANG(
), Guangyi WANG( )
)
- 1 School of Electronic and Information, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310018, China
-
Received:2021-09-27Online:2023-04-18Published:2023-04-18 -
Contact:Yan LIANG E-mail:liangyan@hdu.edu.cn;luzhz@hdu.edu.cn;wanggyi@163.com -
About author:
LI Qingjian was born in 2000. He received his B.E. degree from Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou, China, in 2021. He is currently pursuing his M.S. degree at the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. His research interests include nonlinear dynamics, memristive systems, and neural networks.E-mail: lqj@hdu.edu.cn
LIANG Yan was born in 1988. She received her B.E. and Ph.D. degrees from the School of Information and Electrical Engineering, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, in 2011 and 2017, respectively. She is an associate professor with Hangzhou Dianzi University. Her current research interests include memristive systems, nonlinear dynamics, and artificial neural network. E-mail: liangyan@hdu.edu.cn
LU Zhenzhou was born in 1993. He received his B.E. and M.S. degrees from the School of Information and Electrical Engineering, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, in 2011 and 2014, respectively. He is currently an engineer with Hangzhou Dianzi University. His current research interests include nonlinear dynamics, memristive systems, intrinsic safety, and wireless power transmission. E-mail: luzhz@hdu.edu.cn
WANG Guangyi was born in 1957. He received his Ph.D. degree in electronic science and technology from the South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, in 2004. From 1996 to 2003, he was a professor with the Physics Department, Binzhou University. Since 2004, he has been a professor with the School of Electronic Information, Hangzhou Dianzi University. He is the author of two books, over 110 articles, with over 20 granted patents. His research interests include nonlinear dynamics, chaotic circuits, and memristive circuits. E-mail: wanggyi@163.com -
Supported by:This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61801154;61771176), and the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY20F010008)
引用本文
. [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 34(2): 324-334.
Qingjian LI, Yan LIANG, Zhenzhou LU, Guangyi WANG. Threshold-type memristor-based crossbar array design and its application in handwritten digit recognition[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 34(2): 324-334.
"
| Parameter | Value |
| GL/S | 10−3 |
| GH/S | 9×10−3 |
| k | 0.1 |
| p | 2 |
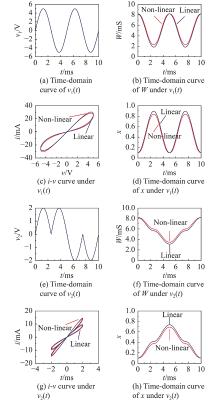
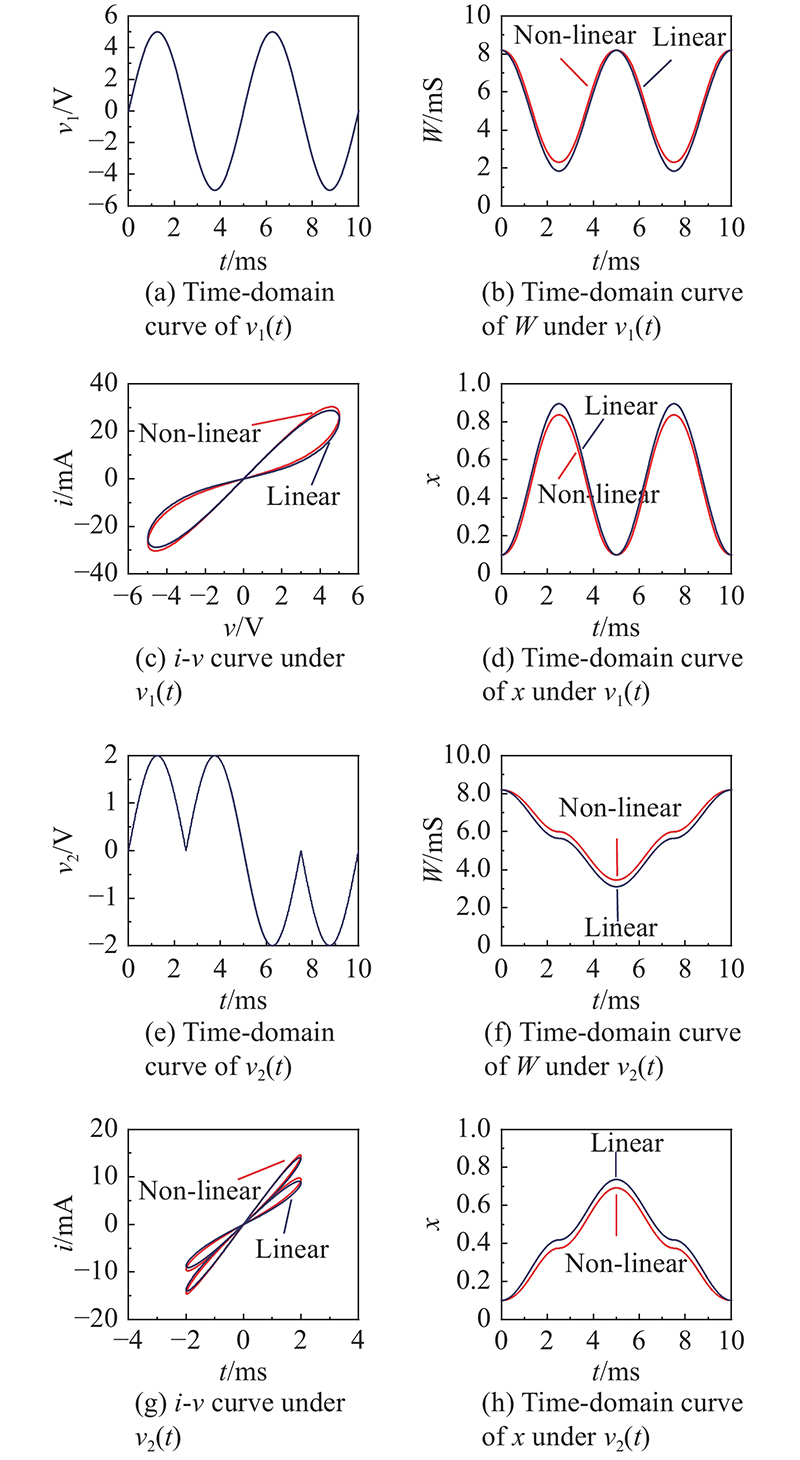
| v1(t)/V | 5sin(400πt) |
| v2(t)/V | |
"
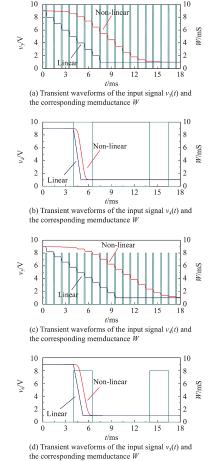
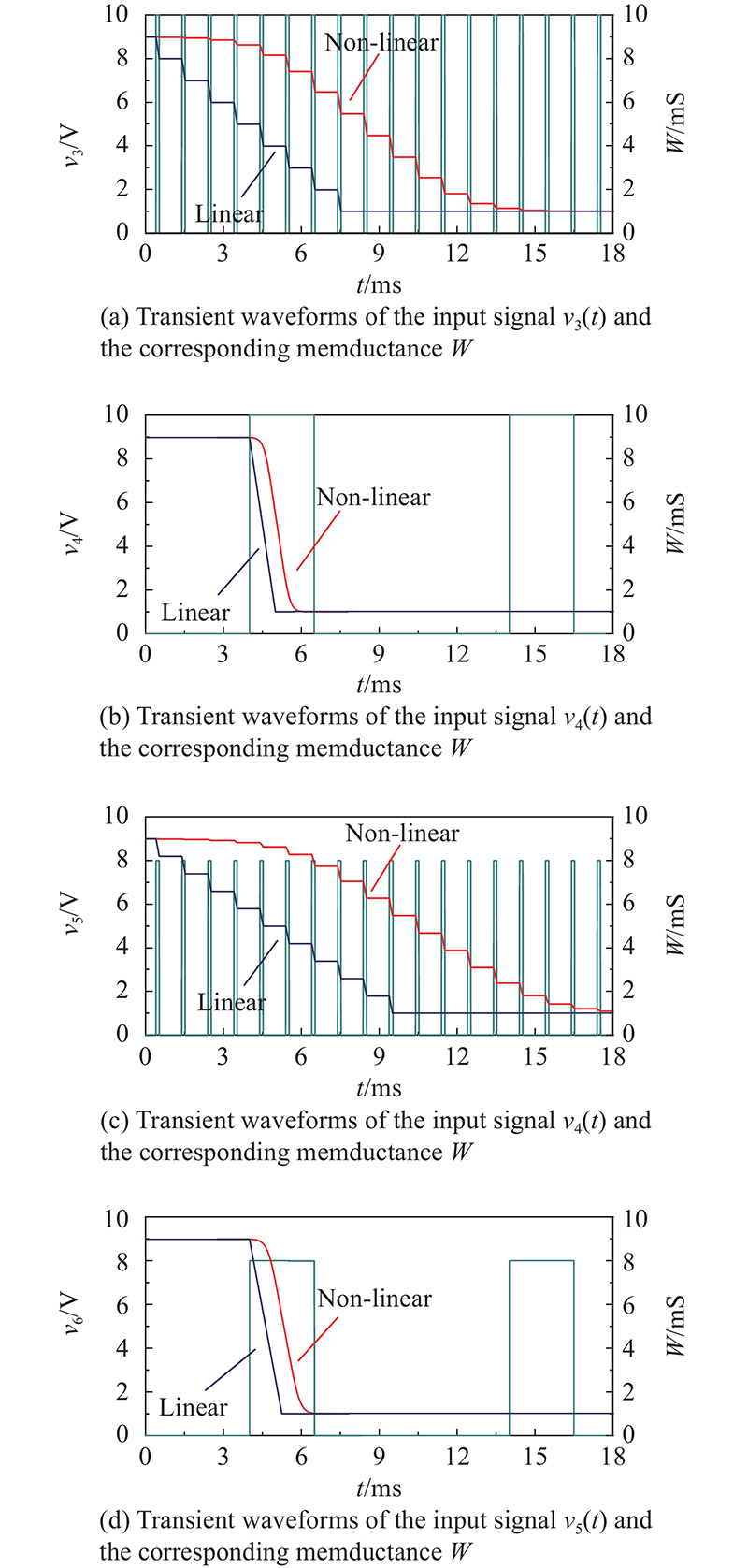
| Memristor number | Before | Training signal | After | |||
| Amplitude/ V | Period/ μs | Duty/ % | Total time/ ms | |||
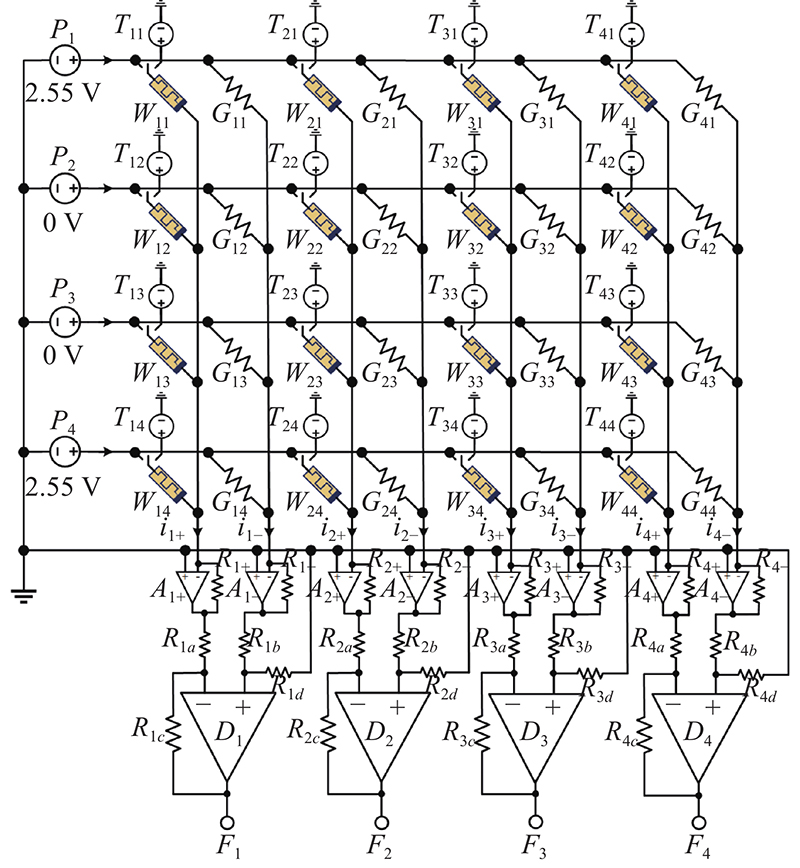
| W11 | 5.1 mS (1) | − | − | − | − | 5.1 mS (1) |
| W12 | 5.1 mS (1) | − | − | − | − | 5.1 mS (1) |
| W13 | 5.1 mS (1) | − | − | − | − | 5.1 mS (1) |
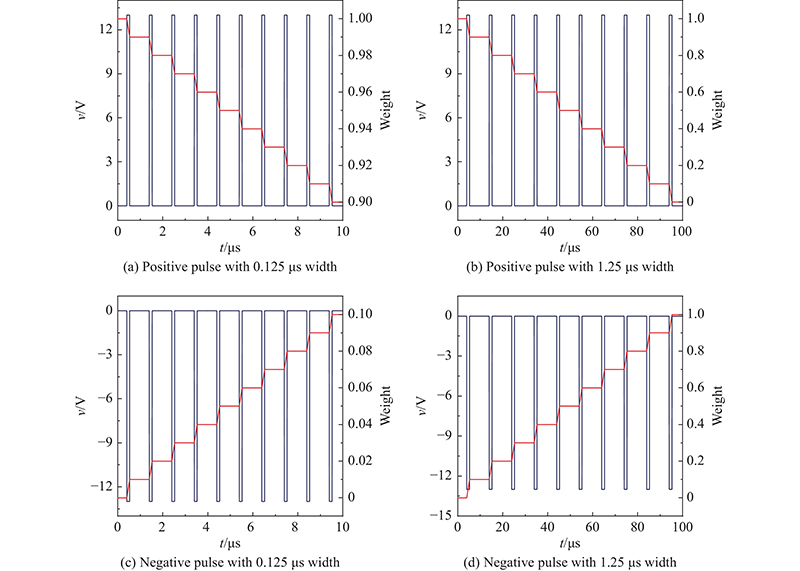
| W14 | 5 mS (0) | 13 | 10 | 12.5 | 0.1 | 4.9 mS (−1) |
| W21 | 5 mS (0) | 13 | 10 | 12.5 | 0.1 | 5.1 mS (1) |
| W22 | 5.1 mS (1) | − | − | − | − | 5.1 mS (1) |
| W23 | 5.1 mS (1) | − | − | − | − | 5.1 mS (1) |
| W24 | 5 mS (0) | − | − | − | − | 5 mS (0) |
| W31 | 5 mS (0) | − | − | − | − | 5 mS (0) |
| W32 | 5.1 mS (1) | − | − | − | − | 5.1 mS (1) |
| W33 | 5.1 mS (1) | − | − | − | − | 5.1 mS (1) |
| W34 | 5 mS (0) | 13 | 10 | 12.5 | 0.1 | 5.1 mS (1) |
| W41 | 5 mS (0) | 13 | 10 | 12.5 | 0.1 | 4.9 mS (−1) |
| W42 | 5.1 mS (1) | − | − | − | − | 5.1 mS (1) |
| W43 | 5.1 mS (1) | − | − | − | − | 5.1 mS (1) |
| W44 | 5.1 mS (1) | − | − | − | − | 5.1 mS (1) |
| 1 |
MA C, LUO Z, HUANG W C, et al Sub-nanosecond memristor based on ferroelectric tunnel junction. Nature Communications, 2020, 11 (1): 1439.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15249-1 |
| 2 |
SERB A, CORNA A, GEORGE R, et al Memristive synapses connect brain and silicon spiking neurons. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10 (1): 32098971.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58831-9 |
| 3 |
ZHU R H, TANG Z R, YE S Z, et al Memristor-based image enhancement: high efficiency and robustness. IEEE Trans. on Electron Devices, 2021, 68 (2): 602- 609.
doi: 10.1109/TED.2020.3045684 |
| 4 |
NAWROCKI R A, VOYLES R M, SHAHEEN S E A mini review of neuromorphic architectures and implementations. IEEE Trans. on Electron Devices, 2016, 63 (10): 3819- 3829.
doi: 10.1109/TED.2016.2598413 |
| 5 |
WANG J R, ZHUGE F Memristive synapses for brain-inspired computing. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2019, 4 (3): 1800544.
doi: 10.1002/admt.201800544 |
| 6 |
HUANG W, XIA X W, ZHU C, et al Memristive artificial synapses for neuromorphic computing. Nano-Micro Letters, 2021, 13 (1): 34138298.
doi: 10.1007/s40820-021-00618-2 |
| 7 |
MEAD C Neuromorphic electronic systems. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1990, 78 (10): 1629- 1636.
doi: 10.1109/5.58356 |
| 8 |
MARKOVIC D, MIZRAHI A, QUERLIOZ D, et al Physics for neuromorphic computing. Nature Reviews Physics, 2020, 2, 499- 510.
doi: 10.1038/s42254-020-0208-2 |
| 9 |
CHUA L O Memristor—the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. on Circuit Theory, 1971, 18 (5): 507- 519.
doi: 10.1109/TCT.1971.1083337 |
| 10 |
CHUA L O The fourth element. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100 (6): 1920- 1927.
doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2012.2190814 |
| 11 |
STRUKOV D, SNIDER G, STEWART D, et al The missing memristor found. Nature, 2008, 453 (7191): 80- 83.
doi: 10.1038/nature06932 |
| 12 |
MEHONIC A, SEBASTIAN A, RAJENDRAN B, et al Memristors from in-memory computing, deep learning acceleration, and spiking neural networks to the future of neuromorphic and bio-inspired computing. Advanced Intelligent Systems, 2020, 2 (11): 2000085.
doi: 10.1002/aisy.202000085 |
| 13 |
LIU Z W, TANG J S, GAO B, et al Neural signal analysis with memristor arrays towards high-efficiency brain-machine interfaces. Nature Communications, 2020, 11 (1): 32843643.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13993-7 |
| 14 |
XIA Q, YANG J J Memristive crossbar arrays for brain-inspired computing. Nature Materials, 2019, 18 (4): 309- 323.
doi: 10.1038/s41563-019-0291-x |
| 15 |
GIBSON G A, MUSUNURU S, ZHANG J Nanocsale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems. Nano Letters, 2010, 10 (4): 1297- 1301.
doi: 10.1021/nl904092h |
| 16 |
KIM H, SAH M P, YANG C, et al Memristor bridge synapses. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100 (6): 2061- 2070.
doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2011.2166749 |
| 17 |
KIM H, GABA S, WHEELER D, et al A functional hybrid memristor crossbar-array/CMOS system for data storage and neuromorphic applications. Nano Letters, 2012, 12 (1): 389- 395.
doi: 10.1021/nl203687n |
| 18 |
HU X F, DUAN S K, WANG L D, et al Memristive crossbar array with applications in image processing. Science China Information Sciences, 2012, 55 (2): 461- 472.
doi: 10.1007/s11432-011-4410-9 |
| 19 |
LI C, WANG Z R, RAO M Y, et al Long short-term memory networks in memristor crossbar arrays. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2019, 1 (1): 49- 57.
doi: 10.1038/s42256-018-0001-4 |
| 20 |
YAO P, WU H Q, GAO B, et al Fully hardware-implemented memristor convolutional neural network. Nature, 2020, 577 (7792): 641- 646.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1942-4 |
| 21 |
YU Y B, YANG C Y, DENG Q X, et al Memristive network-based genetic algorithm and its application to image edge detection. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 32 (5): 1062- 1070.
doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2021.000091 |
| 22 |
YU Y B, YANG N J, YANG C Y, et al Memristor bridge-based low pass filter for image processing. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 30 (3): 448- 455.
doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2019.03.02 |
| 23 |
LIN P, LI C, WANG Z R, et al Three-dimensional memristor circuits as complex neural networks. Nature Electronics, 2020, 3 (4): 225- 232.
doi: 10.1038/s41928-020-0397-9 |
| 24 |
HU M, LI H, CHEN Y R, et al Memristor crossbar-based neuromorphic computing system: a case study. IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25 (10): 1864- 1878.
doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2296777 |
| 25 | LIU Q, WANG L D, DUAN S K An adaptive three-Gauss model based on memristive cross array and its application in image enhancement. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66 (12): 300- 310. |
| 26 | ANDERSON D, MCNEILL G Artificial neural networks technology. Kaman Sciences Corporation, 1992, 258 (6): 22- 25. |
| 27 |
JOGLEKAR Y N, WOLF S J The elusive memristor: properties of basic electrical circuits. European Journal of Physics, 2009, 30 (4): 661- 675.
doi: 10.1088/0143-0807/30/4/001 |
| 28 | PERSHIN Y V, VENTRA M D SPICE model of memristive devices with threshold. Radioengineering, 2013, 22 (2): 485- 489. |
| 29 |
KVATINSKY S, RAMADAN M, FRIEDMAN E G, et al VTEAM: a general model for voltage-controlled memristors. IEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems II-Express Briefs, 2015, 62 (8): 786- 790.
doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2015.2433536 |
| 30 |
SONG S, MILLER K D, ABBOTT L F Competitive hebbian learning through spike-timing-dependent synaptic plasticity. Nature Neuroscience, 2000, 3 (9): 919- 926.
doi: 10.1038/78829 |
| 31 |
ZHAN C X, CHEN Y, YI M D, et al Recent progress in memristors for stimulating synaptic plasticity. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2018, 48 (2): 115- 142.
doi: 10.1360/N112017-00022 |
| 32 | SCHUMAN C D, POTOK T E, PATTON R M, et al. A survey of neuromorphic computing and neural networks in hardware. https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.06963. |
| 33 | HAN J, MORAGA C The influence of the sigmoid function parameters on the speed of back propagation learning. Proc. of the International Workshop on Artificial Neural Networks, 1995, 930, 195- 201. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||