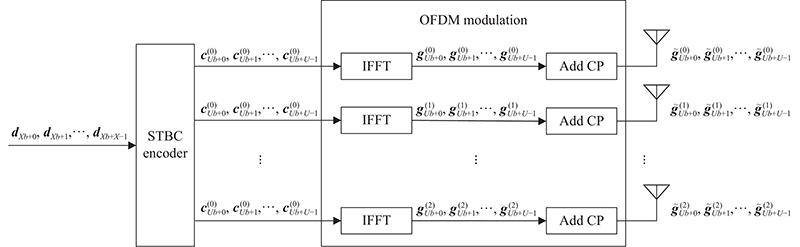
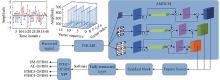
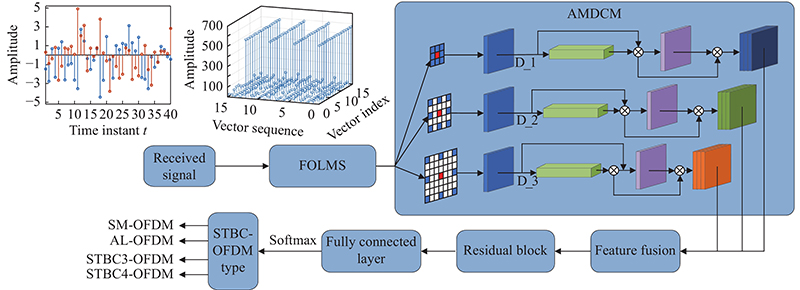
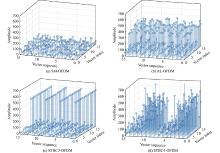
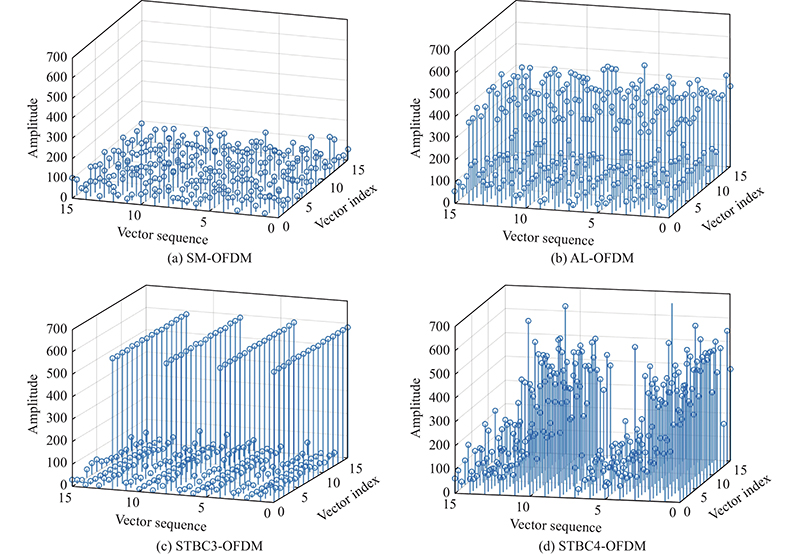
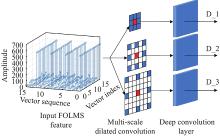
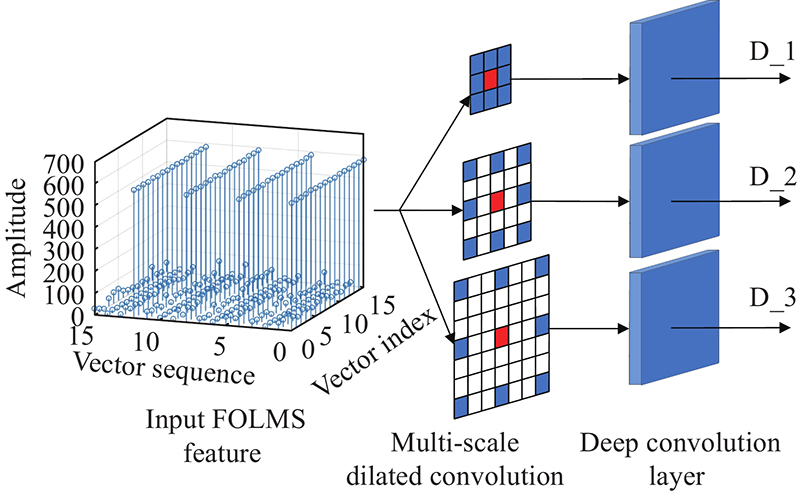
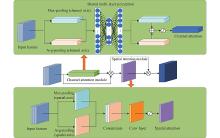
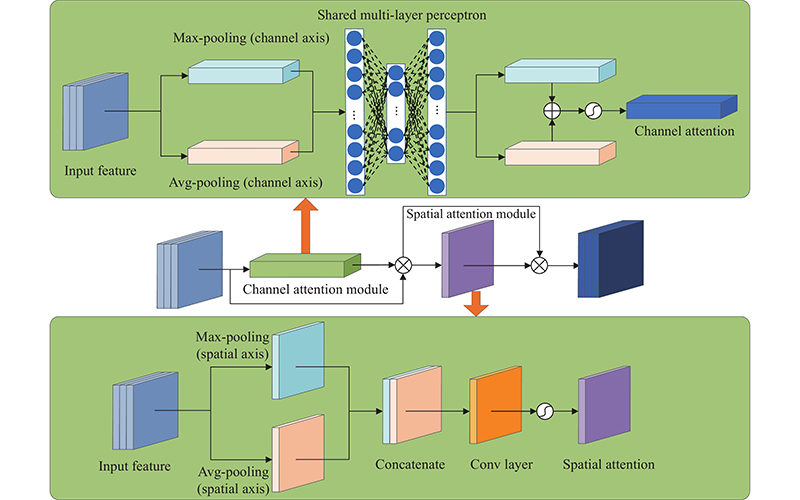
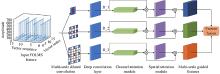
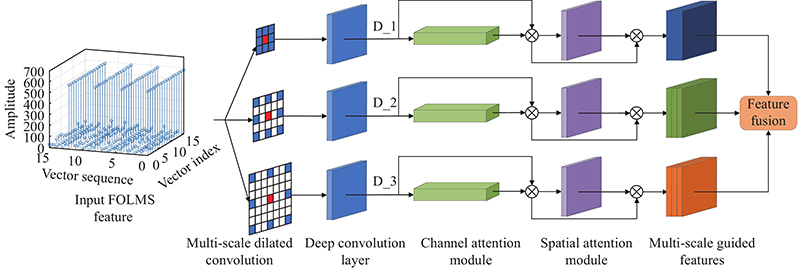
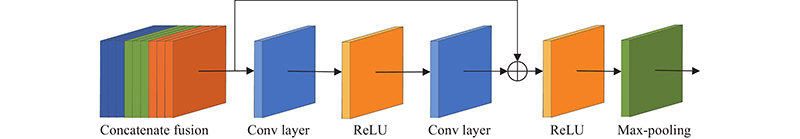
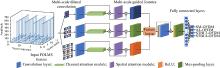
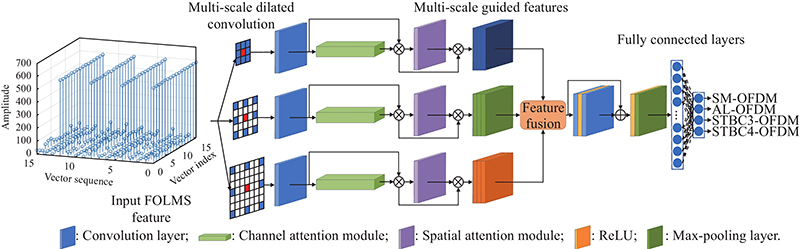
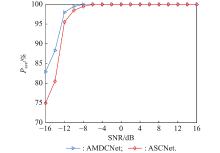
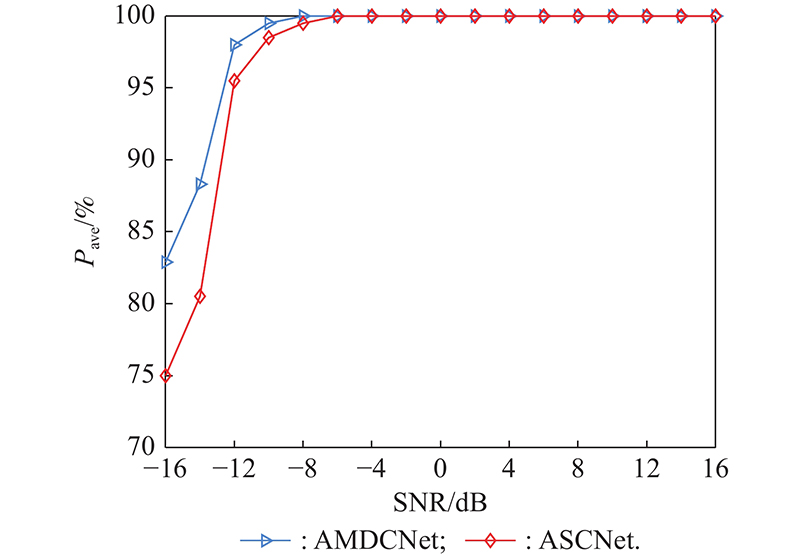
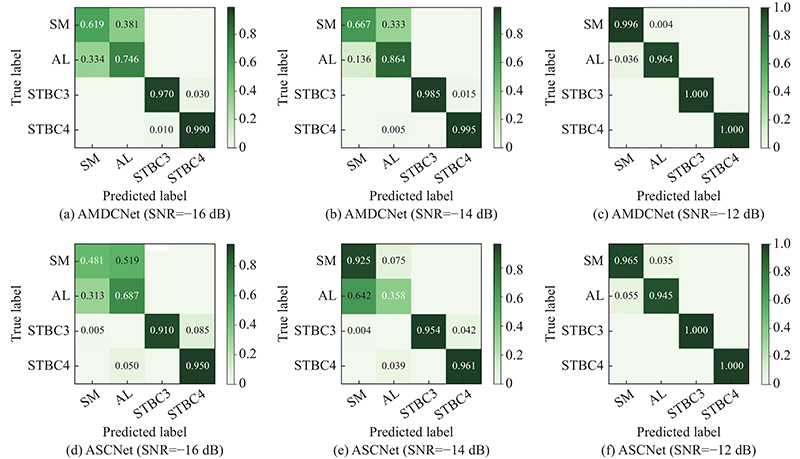
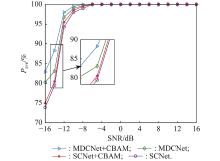
Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2023, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 307-323.doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2023.000027
• • 上一篇
-
收稿日期:2021-07-16出版日期:2023-04-18发布日期:2023-04-18
FOLMS-AMDCNet: an automatic recognition scheme for multiple-antenna OFDM systems
Yuyuan ZHANG( ), Wenjun YAN(
), Wenjun YAN( ), Limin ZHANG(
), Limin ZHANG( ), Qing LING(
), Qing LING( )
)
- 1 Academy of Aeronautical Operations Service, Naval Aviation University, Yantai 264001, China
-
Received:2021-07-16Online:2023-04-18Published:2023-04-18 -
Contact:Wenjun YAN E-mail:2932484433@qq.com;wj_yan@foxmail.com;iamzlm@163.com;lingqing19870522@163.com -
About author:
ZHANG Yuyuan was born in 1997. He received his B.S. degree from Naval Aviation University, Yantai, China, in 2019, where he is currently pursuing his M.S. degree. His current research interests include signal processing, blind identification of channel coding, and deep learning. E-mail: 2932484433@qq.com
YAN Wenjun was born in 1986. He received his M.S. and Ph.D. degrees from Naval Aviation University, Yantai, China, in 2015, where he is currently an associate professor. His current research interests include signal processing, cognitive radio, deep reinforcement learning, and the blind identification of channel coding. E-mail: wj_yan@foxmail.com
ZHANG Limin was born in 1966. He received his Ph.D. degree from Tanjin University, Tanjin, China, in 2005. He is currently a professor and a Ph.D. supervisor with Naval Aviation University, Yantai, China. His current research interests include signal processing, deep learning, blind identification of channel coding, and satellite reconnaissance. E-mail: iamzlm@163.com
LING Qing was born in 1987. She received her M.S. and Ph.D. degrees from Naval Aviation University, Yantai, China, in 2016, where she is currently an associate professor. Her current research interests include signal processing, cognitive radio, and wireless communication. E-mail: lingqing19870522@163.com -
Supported by:This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91538201) and the Taishan Scholar Foundation of China (ts201511020).
引用本文
. [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 34(2): 307-323.
Yuyuan ZHANG, Wenjun YAN, Limin ZHANG, Qing LING. FOLMS-AMDCNet: an automatic recognition scheme for multiple-antenna OFDM systems[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 34(2): 307-323.
| 1 |
MEHRABI M, MOHAMMADKARIMI M, ARDAKANI M, et al Decision directed channel estimation based on deep neural network k-step predictor for MIMO communications in 5G. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37 (11): 2443- 2456.
doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2934004 |
| 2 | ELDEMERDASH Y A, DOBRE O A, ONER M Signal identification for multiple-antenna wireless systems: achievements and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2016, 18 (3): 1524- 1551. |
| 3 | ELDEMERDASH Y A, DOBRE O A, LIAO B J Blind identification of SM and alamouti STBC-OFDM signals. IEEE Trans. on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14 (2): 942- 982. |
| 4 |
KARAMI E, DOBRE O A Identification of SM-OFDM and AL-OFDM signals based on their second-order cyclostationarity. IEEE Trans. on Vehicular Technology, 2015, 64 (3): 942- 953.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2014.2326107 |
| 5 | YAN W J, ZHANG L M, LING Q A method for blind recognition of STBC-OFDM signals based on FOLP. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45 (9): 2233- 2240. |
| 6 | MAREY M, DOBRE O A, INKOL R Novel algorithm for STBC-OFDM identification in cognitive radios. Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Communications, 2013, 2770- 2774. |
| 7 |
MAREY M, DOBRE O A, INKOL R Blind STBC identification for multiple-antenna OFDM systems. IEEE Trans. on Communications, 2014, 62 (5): 1554- 1567.
doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2014.030214.130875 |
| 8 | ZHANG L M, YU K Y, YAN W J, et al. Blind identification algorithm of time-domain STBC-OFDM based on feature sequence. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(8): 1524−1532. (in Chinese) |
| 9 |
ZENG Z G, CHEN X H, SONG Z H MGFN: a multi-granularity fusion convolutional neural network for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 76038- 76046.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3081922 |
| 10 |
LI S Y, CHEN Y W, JIANG R X, et al Image denoising via multi-scale gated fusion network. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 49392- 49402.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2910879 |
| 11 |
JIANG Y, TAN N, PENG T T, et al Retinal vessels segmentation based on dilated multi-scale convolutional neural network. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 76342- 76352.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2922365 |
| 12 |
TIAN Y L, ZHANG Q S, REN Z L, et al Multi-scale dilated convolution network based depth estimation in intelligent transportation systems. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 185179- 185188.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2960520 |
| 13 |
NIU Y L, LU Z W, WEN J, et al Multi-modal multi-scale deep learning for large-scale image annotation. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing, 2019, 28 (4): 1720- 1731.
doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2881928 |
| 14 |
LAI R, LI Y X, GUAN J T, et al Multi-scale visual attention deep convolutional neural network for multi-focus image fusion. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 114385- 114399.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2935006 |
| 15 | WEN C R, HONG M J, YANG X H, et al Pulmonary nodule detection based on convolutional block attention module. Proc. of the Chinese Control Conference, 2019, 8583- 8587. |
| 16 |
HUANG G Y, GONG Y Y, XU Q Z, et al A convolutional attention residual network for stereo matching. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 50828- 50842.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2980243 |
| 17 |
ZHOU S P, WANG J J, ZHANG J, et al Hierarchical U-shape attention network for salient object detection. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing, 2020, 29, 8417- 8428.
doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3011554 |
| 18 | SUN J, XIA S Y, SUN Z L, et al Cross-model deep feature fusion for face detection. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2020, 4 (9): 7003304. |
| 19 |
WANG Z J, CHEN B, LU R Y, et al FusionNet: an unsupervised convolutional variational network for hyperspectral and multispectral image fusion. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing, 2020, 29, 7565- 7577.
doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3004261 |
| 20 |
SHEN T Y, WANG J, GOU C, et al Hierarchical fused model with deep learning and type-2 fuzzy learning for breast cancer diagnosis. IEEE Trans. on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 28 (12): 3204- 3218.
doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3013681 |
| 21 |
LIU C, ZHOU W J, CHEN Y Z, et al Asymmetric deeply fused network for detecting salient objects in RGB-D images. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27, 1620- 1624.
doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.3023349 |
| 22 |
WANG H F, LI J F Human action recognition algorithm based on multi-feature map fusion. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 150945- 150954.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3017076 |
| 23 |
ZHAO Y F, XIE K, ZOU Z Z, et al Intelligent recognition of fatigue and sleepiness based on inceptionV3-LSTM via multi-feature fusion. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 144205- 144217.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3014508 |
| 24 |
LIU X M, YU A, WEI X K, et al Multimodal MR image synthesis using gradient prior and adversarial learning. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2020, 14 (6): 1176- 1188.
doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2020.3013418 |
| 25 |
HUANG G H, CHEN X P, CHEN J N, et al Multi-person pose estimation under complex environment based on progressive rotation correction and multi-scale feature fusion. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 132514- 132526.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3010257 |
| 26 |
ZHOU H C, ZHU Y N, WNAG Q, et al Multi-scale dilated convolution neural network for image artifact correction of limited-angle tomography. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 1567- 1576.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2962071 |
| 27 |
GAO H M, CHEN Z H, LI C M Hierarchical shrinkage multiscale network for hyperspectral image classification with hierarchical feature fusion. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14, 5760- 5772.
doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3083283 |
| 28 |
GONG M M, SHU Y M Real-time detection and motion recognition of human moving objects based on deep learning and multi-scale feature fusion in video. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 25811- 25822.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2971283 |
| 29 |
GAO A, ZHU Y L, CAI W H, et al Pattern recognition of partial discharge based on VMD-CWD spectrum and optimized CNN with cross-layer feature fusion. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 151296- 151306.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3017047 |
| 30 |
SUN L, YANG K L, HU X X, et al Real-time fusion network for RGB-D semantic segmentation incorporating unexpected obstacle detection for road-driving images. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5 (4): 5558- 5565.
doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.3007457 |
| 31 |
CHEN H, DENG Y J, LI Y F, et al RGBD salient object detection via disentangled cross-modal fusion. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing, 2020, 29, 8407- 8416.
doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3014734 |
| 32 |
CUI S E, WANG R, WEI J H, et al Self-attention based visual-tactile fusion learning for predicting grasp outcomes. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5 (4): 5827- 5834.
doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.3010720 |
| 33 |
DONG X H, ZHOU H Y, DONG J Y Texture classification using pair-wise difference pooling-based bilinear convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing, 2020, 29, 8776- 8790.
doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3019185 |
| 34 |
LI C X, HANG R L, RASTI B EMFNet: enhanced multisource fusion network for land cover classification. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14, 4381- 4389.
doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3073719 |
| 35 |
YE X C, SUN B L, WANG Z H, et al PMBANet: progressive multi-branch aggregation network for scene depth super-resolution. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing, 2020, 29, 7427- 7442.
doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3002664 |
| 36 |
LIU Y S, LIU Y B, DING L W, et al Scene classification based on two-stage deep feature fusion. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15 (2): 183- 186.
doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2779469 |
| 37 |
ZHANG Z F, WANG C, GAN C Q, et al Automatic modulation classification using convolutional neural network with features fusion of SPWVD and BJD. IEEE Trans. on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, 2019, 5 (3): 469- 478.
doi: 10.1109/TSIPN.2019.2900201 |
| 38 |
MA J T, QIU T S Automatic modulation classification using cyclic correntropy spectrum in impulsive noise. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8 (2): 440- 443.
doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2875001 |
| 39 |
WU H, LI Y X, ZHOU L, et al Convolutional neural network and multi-feature fusion for automatic modulation classification. IET Electronics Letters, 2019, 55 (16): 895- 897.
doi: 10.1049/el.2019.1789 |
| 40 |
WANG Y, LIU M, YANG J, et al Data-driven deep learning for automatic modulation recognition in cognitive radios. IEEE Trans. on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68 (4): 4074- 4077.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2900460 |
| 41 |
YAN X, ZHANG G Y, WU H A novel automatic modulation classifier using graph-based constellation analysis for M-ary QAM. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23 (2): 298- 301.
doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2889084 |
| 42 |
WANG Y, GUI J, YIN Y, et al Automatic modulation classification for MIMO systems via deep learning and zero-forcing equalization. IEEE Trans. on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69 (5): 5688- 5692.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2981995 |
| 43 |
GHASEMZADEH P, BANERJEE S, HEMPEL M, et al A novel deep learning and polar transformation framework for an adaptive automatic modulation classification. IEEE Trans. on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69 (11): 13243- 13258.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3022394 |
| 44 |
KUMAR Y, SHEORAN M, JAJOO G, et al Automatic modulation classification based on constellation density using deep learning. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24 (6): 1275- 1278.
doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2980840 |
| 45 | ZHENG S L, QI P H, CHEN S C, et al Fusion methods for CNN-based automatic modulation classification. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 66496–66504. |
| 46 |
HERMAWAN A P, GINANJAR R R, KIM D, et al CNN-based automatic modulation classification for beyond 5G communications. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24 (5): 1038- 1041.
doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2970922 |
| 47 |
TU Y, LIN Y, HOU C B, et al Complex-valued networks for automatic modulation classification. IEEE Trans. on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69 (9): 10085- 10089.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3005707 |
| 48 |
WANG Y, WANG J, YANG J, et al Deep learning-based cooperative automatic modulation classification method for MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69 (4): 4575- 4579.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2976942 |
| 49 | SHAH M H, DANG X Novel feature selection method using Bhattacharyya distance for neural networks based automatic modulation classification. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27, 106- 110. |
| 50 | SUN J, XU G L, REN W J, et al Radar emitter classification based on unidimensional convolutional neural network. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12 (8): 862- 867. |
| 51 |
WONG L J, HEADLEY W C, MICHAELS A J Specific emitter identification using convolutional neural network-based IQ imbalance estimators. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 33544- 33555.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2903444 |
| 52 |
PAN Y W, YANG S H, PENG H, et al Specific emitter identification based on deep residual networks. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 54425- 54434.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2913759 |
| 53 |
DING L D, WANG S L, WANG F G, et al Specific emitter identification via convolutional neural networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22 (12): 2591- 2594.
doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2871465 |
| 54 |
HE B X, WANG F G Cooperative specific emitter identification via multiple distorted receivers. IEEE Trans. on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15, 3791- 3806.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2020.3001721 |
| 55 | BAI J L, GAO L, GAO J P, et al A new radar signal modulation recognition algorithm based on time-frequency transform. Proc. of the IEEE 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, 2019, 21- 25. |
| 56 |
ZHANG J S, XING M D, XIE Y Y FEC: a feature fusion framework for sar target recognition based on electromagnetic scattering features and deep CNN features. IEEE Trans. on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59 (3): 2174- 2187.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3003264 |
| 57 |
GAO F, SHI W, WANG J, et al A semi-supervised synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image recognition algorithm based on an attention mechanism and bias-variance decomposition. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 108617- 108632.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2933459 |
| 58 |
XIONG G, XI Y L, CHEN D, et al Dual-polarization SAR ship target recognition based on mini hourglass region extraction and dual-channel efficient fusion network. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 29078- 29089.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3058188 |
| 59 |
WEN Z D, WU Q, LIU Z G, et al Polar-spatial feature fusion learning with variational generative-discriminative network for PolSAR classification. IEEE Trans. on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57 (11): 8914- 8927.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2923738 |
| 60 | YU F, KOLTUN V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.07122. |
| 61 | WOO S, PARK J, LEE J, et al CBAM: convolutional block attention module. Proc. of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2018, 3- 19. |
| 62 | ZHAO S K, NGUYEN T H, MA B Monaural speech enhancement with complex convolutional block attention module and joint time frequency losses. Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 2021, 6648- 6652. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||