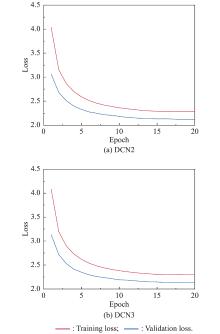
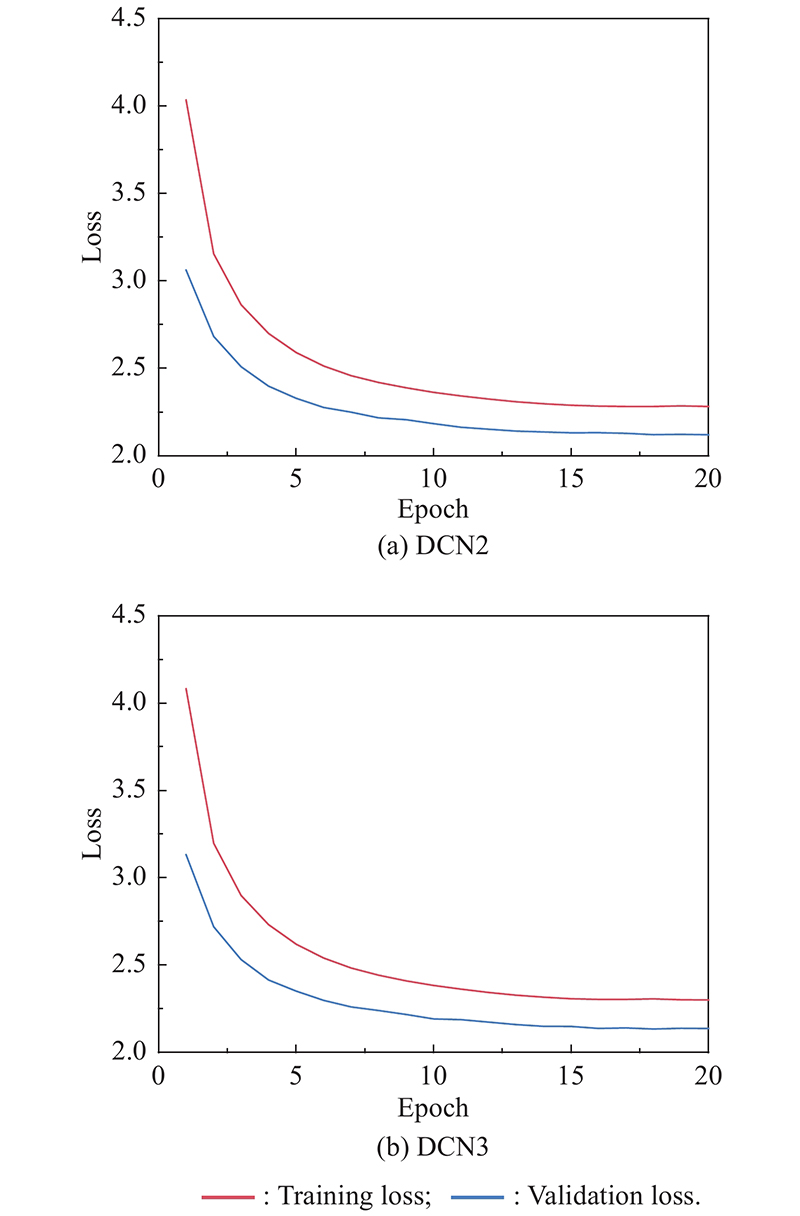
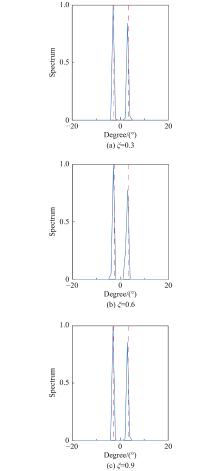
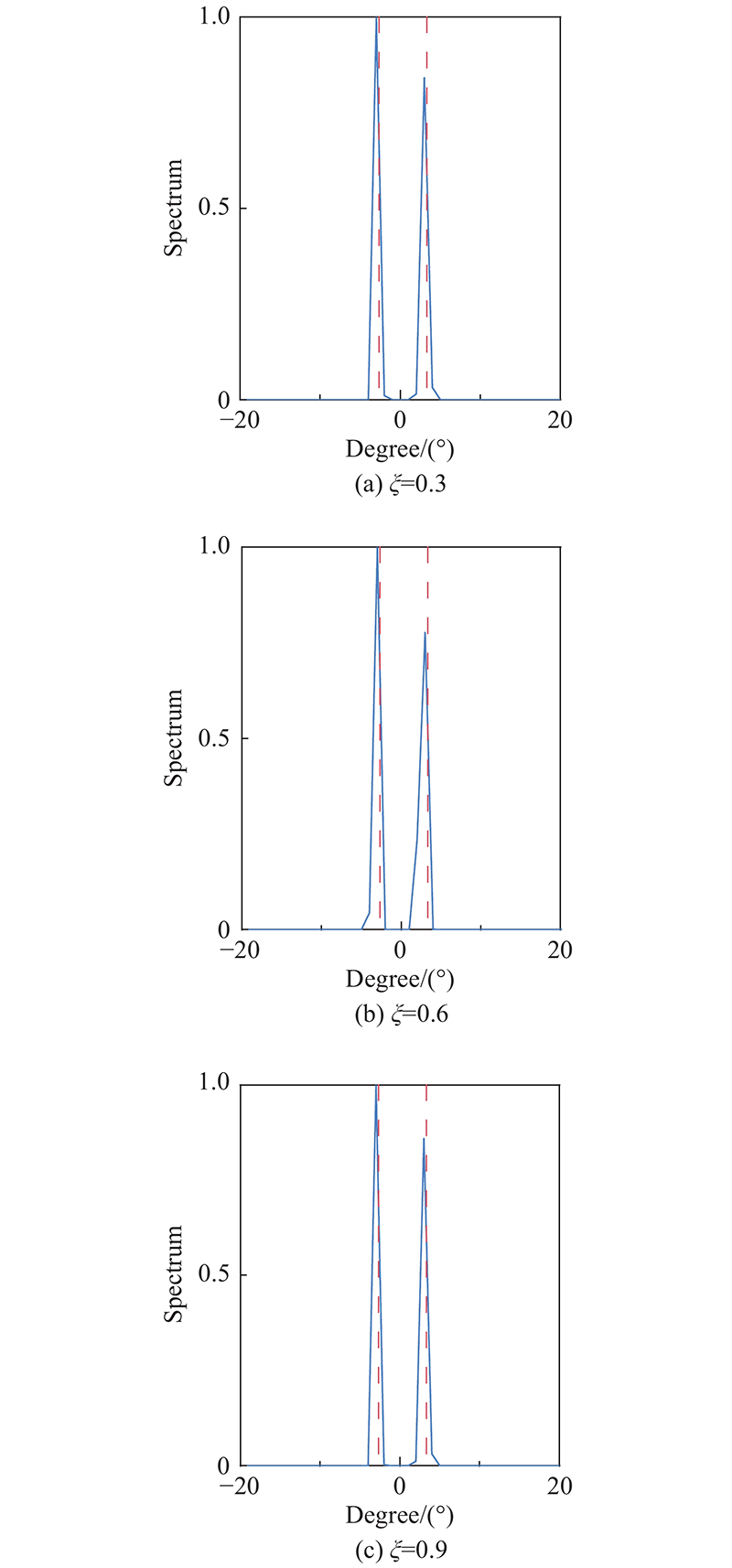
| 1 |
KRIM H, VIBERG M Two decades of array signal processing research: the parametric approach. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 1996, 13 (4): 67- 94.
doi: 10.1109/79.526899
|
| 2 |
DHOPE T S, SIMUNIC D, ZENTNER R Comparison of DOA estimation algorithms in SDMA system. Automatika, 2013, 54 (2): 199- 209.
doi: 10.7305/automatika.54-2.131
|
| 3 |
WU S, YUAN Y, HUANG L, et al Grid-less DOA estimation of coherent sources based on the covariance matrix recovery. Physical Communication, 2021, 46, 101345- 101352.
doi: 10.1016/j.phycom.2021.101345
|
| 4 |
YUAN Y, WU S, YANG Y, et al Multi-DOA estimation based on the KR image tensor and improved estimation network. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11 (1): 6386.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85864-5
|
| 5 |
SCHMIDT R Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34 (3): 276- 280.
doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830
|
| 6 |
ROY R, KAILATH T ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques. IEEE Trans. on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37 (7): 984- 995.
doi: 10.1109/29.32276
|
| 7 |
KUNDU D Modified MUSIC algorithm for estimating DOA of signals. Signal Processing, 1996, 48 (1): 85- 90.
doi: 10.1016/0165-1684(95)00126-3
|
| 8 |
LI J F, ZHANG X F Unitary reduced-dimensional estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques for angle estimation in monostatic multiple-input-multiple-output radar with rectangular arrays. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2014, 8 (6): 575- 584.
doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2013.0269
|
| 9 |
XIE W, WEN F, LIU J B, et al Source association, DOA, and fading coefficients estimation for multipath signals. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2017, 65 (11): 2773- 2786.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2669894
|
| 10 |
SHAN T J, WAX M, KAILATH T On spatial smoothing for direction-of-arrival estimation of coherent signals. IEEE Trans. on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1985, 33 (4): 806- 811.
doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1985.1164649
|
| 11 |
PILLAI S U, KWON B H Forward/backward spatial smoothing techniques for coherent signal identification. IEEE Trans. on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37 (1): 8- 15.
doi: 10.1109/29.17496
|
| 12 |
MALIOUTOV D, CETIN M, WILLSKY A S A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2005, 53 (8): 3010- 3022.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.850882
|
| 13 |
LIU Z M, HUANG Z T, ZHOU Y Y Direction-of-arrival estimation of wideband signals via covariance matrix sparse representation. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2011, 59 (9): 4256- 4270.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2159214
|
| 14 |
YANG Z, XIE L, ZHANG C Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2012, 61 (1): 38- 43.
|
| 15 |
STOICA P, SHARMAN K C Maximum likelihood methods for direction-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Trans. on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1990, 38 (7): 1132- 1143.
doi: 10.1109/29.57542
|
| 16 |
CHOI Y H Alternating projection for maximum-likelihood source localization using eigendecomposition. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 1999, 6 (4): 73- 75.
doi: 10.1109/97.752057
|
| 17 |
VIBERG M, OTTERSTEN B, KAILATH T Detection and estimation in sensor arrays using weighted subspace fitting. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 1991, 39 (11): 2436- 2449.
doi: 10.1109/78.97999
|
| 18 |
BRESLER Y, MACOVSKI A Exact maximum likelihood parameter estimation of superimposed exponential signals in noise. IEEE Trans. on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1986, 34 (5): 1081- 1089.
doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1986.1164949
|
| 19 |
STOICA P, SHARMAN K C Novel eigenanalysis method for direction estimation. IEE Proceeding, 1990, 137 (1): 19- 26.
|
| 20 |
ZHU W L, ZHANG M A deep learning architecture for broadband DOA estimation. Proc. of the IEEE 19th International Conference on Communication Technology, 2019, 244- 247.
|
| 21 |
VARANASI V, GUPTA H, HEGDE R M A deep learning framework for robust DOA estimation using spherical harmonic decomposition. IEEE/ACM Trans. on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2020, 28, 1248- 1259.
doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2020.2984852
|
| 22 |
HUANG Z Q, XU J, PAN J L A regression approach to speech source localization exploiting deep neural network. Proc. of the IEEE 4th International Conference on Multimedia Big Data, 2018.
|
| 23 |
PAK J, SHIN J W Sound localization based on phase difference enhancement using deep neural networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2019, 27 (8): 1335- 1345.
doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2019.2919378
|
| 24 |
ZHU W L, ZHANG M, LI P F, et al Two-dimensional DOA estimation via deep ensemble learning. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 124544- 124552.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3005221
|
| 25 |
LIU Z M, ZHANG C, PHILIP S Y Direction-of-arrival estimation based on deep neural networks with robustness to array imperfections. IEEE Trans. on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66 (12): 7315- 7327.
doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2874430
|
| 26 |
ELBIR A M Deepmusic: multiple signal classification via deep learning. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2020, 4 (4): 7001004.
|
| 27 |
WU L, LIU Z M, HUANG Z T Deep convolution network for direction of arrival estimation with sparse prior. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26 (11): 1688- 1692.
doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2945115
|
| 28 |
XIANG H H, CHEN B X, YANG M L, et al Angle separation learning for coherent DOA estimation with deep sparse prior. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25 (2): 465- 469.
doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3032733
|
| 29 |
NAIR V, HINTON G E Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. Proc. of the International Conference on Learning Representations, 2010, 27, 807- 814.
|
| 30 |
IOFFE S, SZEGEDY C Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. Proc. of the International Conference on Learning Representations, 2015, 2, 448- 456.
|
| 31 |
GAL Y, GHAHRAMANI Z. Dropout as a Bayesian approximation: representing model uncertainty in deep learning. Proc. of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, 2015: 1050–1059.
|
| 32 |
SHORE J, JOHNSON R Axiomatic derivation of the principle of maximum entropy and the principle of minimum cross-entropy. IEEE Trans. on Information Theory, 1980, 26 (1): 26- 37.
doi: 10.1109/TIT.1980.1056144
|
| 33 |
KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. Proc. of the International Conference on Learning Representations, 2014. DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.1412.6980.
|
| 34 |
HAN J, MORAGA C The influence of the sigmoid function parameters on the speed of backpropagation learning. International Workshop on Artificial Neural Networks: from Natural to Artificial Neural Computation, 1995, 930, 195- 201.
|
| 35 |
XU B, WANG N Y, CHEN T Q, et al. Empirical evaluation of rectified activations in convolutional network. Computer Science. https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.00853.
|
 ), Ye YUAN2(
), Ye YUAN2( ), Weike ZHANG2(
), Weike ZHANG2( ), Naichang YUAN2(
), Naichang YUAN2( )
)