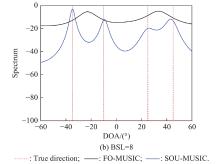
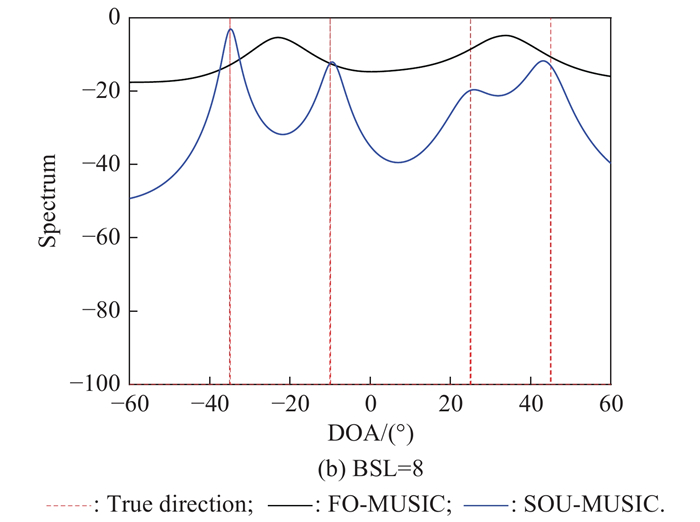
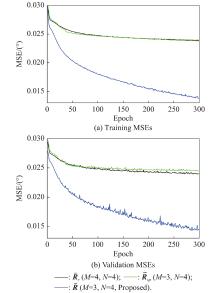
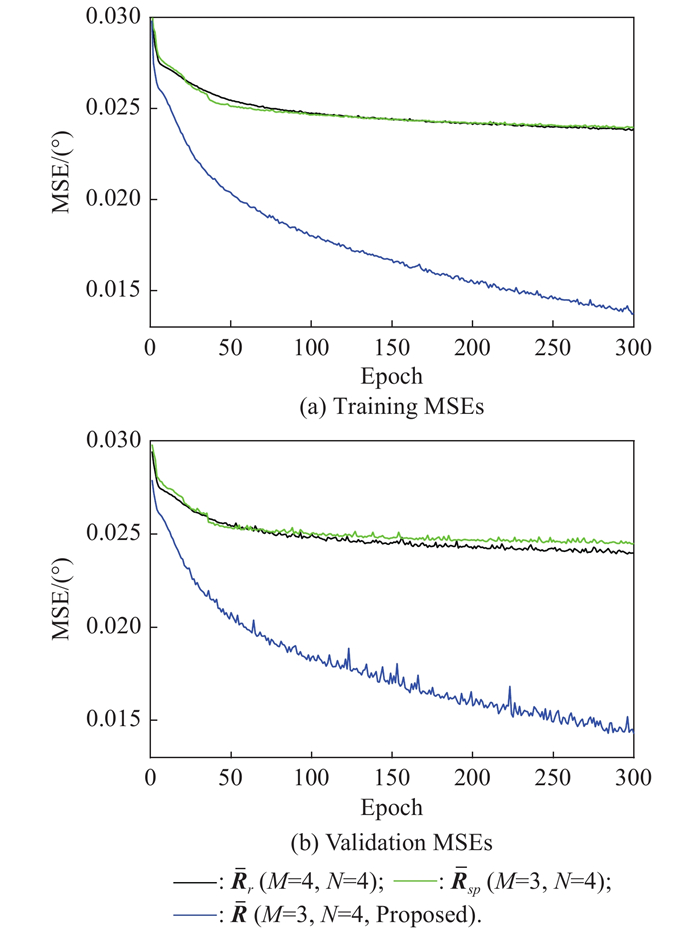
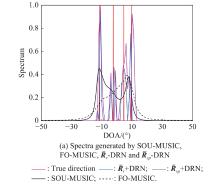
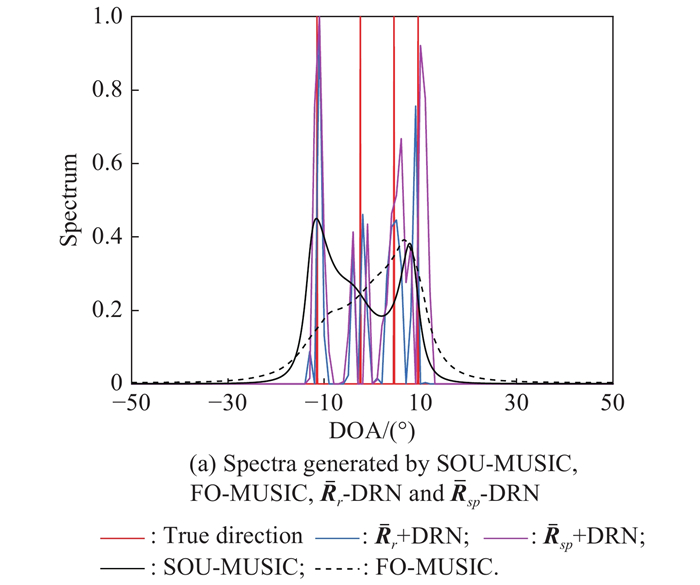
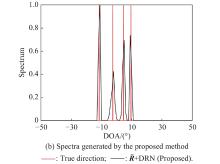
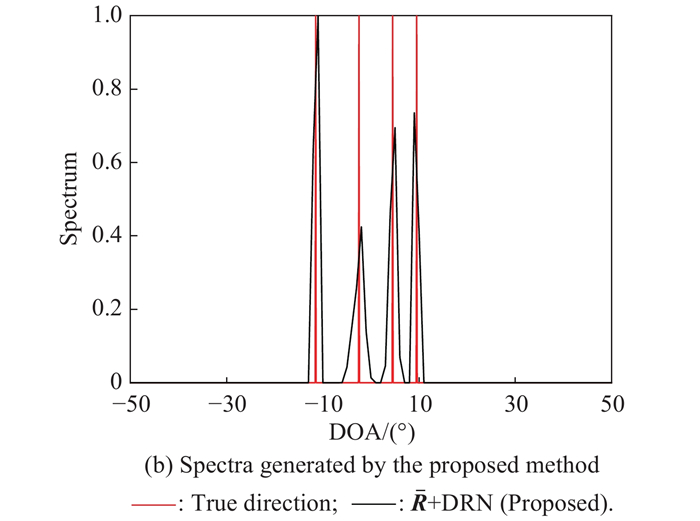
| 1 |
VEEN B V, BUCKLEY K M Beamforming: a versatile approach to spatial filtering. IEEE ASSP Magazine, 2002, 5 (2): 4- 24.
|
| 2 |
LIU Z M, HUANG Z T, ZHOU Y Y An efficient maximum likelihood method for direction-of-arrival estimation via sparse Bayesian learning. IEEE Trans. on Wireless Communications, 2012, 11 (10): 1- 11.
doi: 10.1109/TWC.2012.090312.111912
|
| 3 |
SCHMIDT R, SCHMIDT R O Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34 (3): 276- 280.
doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830
|
| 4 |
ROY R, PAULRAJ A, KAILATH T ESPRIT—a subspace rotation approach to estimation of parameters of cisoids in noise. IEEE Trans. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 1986, 34 (5): 1340- 1342.
doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1986.1164935
|
| 5 |
YIN J H, CHEN T Q Direction-of-arrival estimation using a sparse representation of array covariance vectors. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2011, 59 (9): 4489- 4493.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2158425
|
| 6 |
LIU Z M, HUANG Z T, ZHOU Y Y Sparsity-inducing direction finding for narrowband and wideband signals based on array covariance vectors. IEEE Trans. on Wireless Communications, 2013, 12 (8): 3896- 3907.
|
| 7 |
PORAT B, FRIEDLANDER B Direction finding algorithms based on high-order statistics. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 1991, 39 (9): 2016- 2024.
doi: 10.1109/78.134434
|
| 8 |
CHEVALIER P, FERREOL A, ALBERA L High-resolution direction finding from higher order statistics: the 2q-MUSIC algorithm. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2006, 54 (8): 2986- 2997.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.877661
|
| 9 |
LIU T H, MENDEL J M A subspace-based direction finding algorithm using fractional lower order statistics. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2001, 49 (8): 1605- 1613.
doi: 10.1109/78.934131
|
| 10 |
RICKARD S, DIETRICH F. DOA estimation of many W-disjoint orthogonal sources from two mixtures using DUET. Proc. of the IEEE 10th Workshop on Statistical Signal and Array Processing, 2000: 311−314.
|
| 11 |
TADAION A A, DERAKHTIAN M, GAZOR S A fast multiple-source detection and localization array signal processing algorithm using the spatial filtering and ML approach. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2007, 55 (5): 1815- 1827.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.890819
|
| 12 |
ZHENG Z, LI G J, TENG Y L 2D DOA estimator for multiple coherently distributed sources using modified propagator. Circuits Systems & Signal Processing, 2012, 31 (1): 255- 270.
|
| 13 |
HAN P, WANG D M, CUI W J, et al Underdetermined direction of arrival estimation of non-circular signals via matrix completion in nested array. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 183717- 183728.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2960533
|
| 14 |
YADAV S K, GEORGE N V Underdetermined direction-of-arrival estimation using sparse circular arrays on a rotating platform. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28, 862- 866.
doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3068713
|
| 15 |
HE W, MOTLICEK P, ODOBEZ J M. Deep neural networks for multiple speaker detection and localization. Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2018: 74−79.
|
| 16 |
HUANG H J, YANG J, HUANG H, et al Deep learning for super-resolution channel estimation and DOA estimation based massive MIMO system. IEEE Trans. on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67 (9): 8549- 8560.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2851783
|
| 17 |
MA N, MAY T, BROWN G J Exploiting deep neural networks and head movements for robust binaural localization of multiple sources in Reverberant environments. IEEE Trans. on Audio Speech and Language Processing, 2017, 7 (19): 123- 132.
|
| 18 |
LIU Z M, ZHANG C W, YU P S Direction-of-arrival estimation based on deep neural networks with robustness to array imperfections. IEEE Trans. on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66 (12): 7315- 7327.
doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2874430
|
| 19 |
ABEYWICKRAMA S, JAYASINGHE L, FU H. RF-based direction finding of UAVs using DNN. Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Communication Systems, 2018: 903−912.
|
| 20 |
XIANG H H, CHEN B X, YANG M L Altitude measurement based on characteristics reversal by deep neural network for VHF radar. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13 (1): 98- 103.
|
| 21 |
XIANG H H, CHEN B X, YANG T Improved de-multipath neural network models with self-paced feature-to-feature learning for DOA estimation in multipath environment. IEEE Trans. on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69 (5): 5068- 5078.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2977894
|
| 22 |
XIANG H H, CHEN B X, YANG M L, et al A novel phase enhancement method for low-angle estimation based on supervised DNN learning. IEEE Access, 2019, 7 (4): 329- 336.
|
| 23 |
WU L L, LIU Z M, HUANG Z T Deep convolution network for direction of arrival estimation with sparse prior. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26 (11): 1688- 1692.
doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2945115
|
| 24 |
GUO Y, ZHANG Z, HUANG Y Z DOA estimation method based on cascaded neural network for two closely spaced sources. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27 (1): 570- 574.
|
| 25 |
CHEN Y, WANG C, XIONG K L. Synchronized perturbation elimination and DOA estimation via signal selection mechanism and parallel deep capsule networks in multipath environment. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2021. DOI: 10.1016/J.CJA.2021.01.016.
|
| 26 |
CONGEDO M, GOUY-PAILLER C, JUTTEN C On the blind source separation of human electroencephalogram by approximate joint diagonalization of second order statistics. Clinical Neurophysiology, 2008, 119 (12): 2677- 2686.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2008.09.007
|
| 27 |
LATHAUWER L D, CASTAING J Blind identification of underdetermined mixtures by simultaneous matrix diagonalization. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2008, 56 (3): 1096- 1105.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.908929
|
| 28 |
ZHU L W, WANG Y, WANG X, et al. Underdetermined direction-of-arrival estimation from second order statistics. Proc. of the 7th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, 2014: 989−993.
|
| 29 |
CHEN Y, XIONG K L, HUANG Z T. Robust direction-of-arrival estimation via sparse representation and deep residual convolutional network for co-prime arrays. Proc. of the IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology, 2020: 514−519.
|
| 30 |
HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition. Proc. of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 770−778.
|
| 31 |
SEGHOUANE A K Asymptotic bootstrap corrections of AIC for linear regression models. Signal Processing, 2010, 90 (1): 217- 224.
doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2009.06.010
|
| 32 |
STOICA P, SELEN Y Model-order selection: a review of information criterion rules. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2004, 21 (4): 36- 47.
doi: 10.1109/MSP.2004.1311138
|
 ), Xiang WANG*(
), Xiang WANG*( ), Zhitao HUANG(
), Zhitao HUANG( )
)